SECTION 9: Compliance, Regulations & Policies
Import–Export Compliance Requirements
What is Import–Export Compliance?
Import–Export Compliance refers to the systematic adherence to all applicable national and international laws, regulations, policies, and documentation standards governing the cross-border movement of goods and services.
It ensures that every trade transaction complies with:
- Customs laws
- Foreign trade policies
- Tax and duty regulations
- Foreign exchange regulations
- Product-specific and country-specific restrictions
Import–Export Compliance is not a one-time activity but a continuous process that spans pre-shipment, shipment, and post-shipment stages.
Why is Import–Export Compliance Important?
-
Prevents Legal Penalties & Financial Losses
Non-compliance can lead to:- Heavy fines and penalties
- Suspension or cancellation of IEC
- Blacklisting by authorities
-
Avoids Shipment Detention or Confiscation
Incorrect declarations or missing documents can result in:- Cargo seizure
- Delays at ports
- Demurrage and detention charges
-
Ensures Smooth Customs Clearance
Compliance enables:- Faster clearance
- Reduced inspections
- Predictable logistics timelines
-
Builds Credibility with Banks & Authorities
Banks, insurers, and government agencies prefer compliant exporters and importers for:- Trade finance
- Export incentives
- Credit facilities
-
Protects Brand Reputation
Consistent compliance builds trust with:- Overseas buyers
- Logistics partners
- Government regulators
Where is Import–Export Compliance Applicable?
Import–Export Compliance applies across multiple authorities and checkpoints:
Regulatory Bodies
- Customs Authorities
- DGFT (Directorate General of Foreign Trade)
- GST Authorities
- RBI (Foreign Exchange Management)
Operational Areas
- Ports, Airports, ICDs, SEZs
- Banking channels
- Logistics & freight forwarding operations
Trade Scope
- Physical goods exports/imports
- Service exports
- E-commerce cross-border trade
Core Elements of Import–Export Compliance
-
Accurate Documentation & Declarations
- Correct
- Complete
- Consistent across platforms
Key documents include:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading / Airway Bill
- Bill of Entry / Shipping Bill
-
HS Code Classification
- Customs duty
- Export incentives
- Restrictions or prohibitions
Wrong classification may lead to:
- Duty shortfall demands
- Penalties
- Incentive rejection
-
Foreign Exchange Compliance
- Adherence to FEMA & RBI guidelines
- Timely realization of export proceeds
- Proper reporting through banks
-
Product-Specific Regulations
- Special licenses
- Quality certifications
- Safety or environmental approvals
How to Ensure Import–Export Compliance Effectively
-
Step 1: Business & Product Registration
- IEC registration
- GST registration (where applicable)
-
Step 2: Product Classification & Licensing
- Identify correct HS code
- Check import/export restrictions
-
Step 3: Documentation Preparation
- Accurate invoices
- Transparent declarations
- Digital record keeping
-
Step 4: Customs Filing & Verification
- Shipping Bill / Bill of Entry filing
- Compliance with valuation norms
-
Step 5: Duty, Tax & Incentive Management
- Correct duty calculation
- Timely incentive claims
-
Step 6: Post-Clearance Audit & Record Maintenance
- Retain records for audits
- Ensure consistency across filings
Common Import–Export Compliance Risks
- Incorrect HS code selection
- Under-valuation or over-valuation
- Missing licenses or certificates
- Delayed foreign exchange realization
- Non-adherence to product standards
Best Practices for Strong Compliance Framework
- Maintain updated regulatory knowledge
- Use digital compliance management tools
- Train staff regularly
- Conduct internal compliance audits
- Coordinate closely with CHA & banks
Flowchart – Import–Export Compliance Process
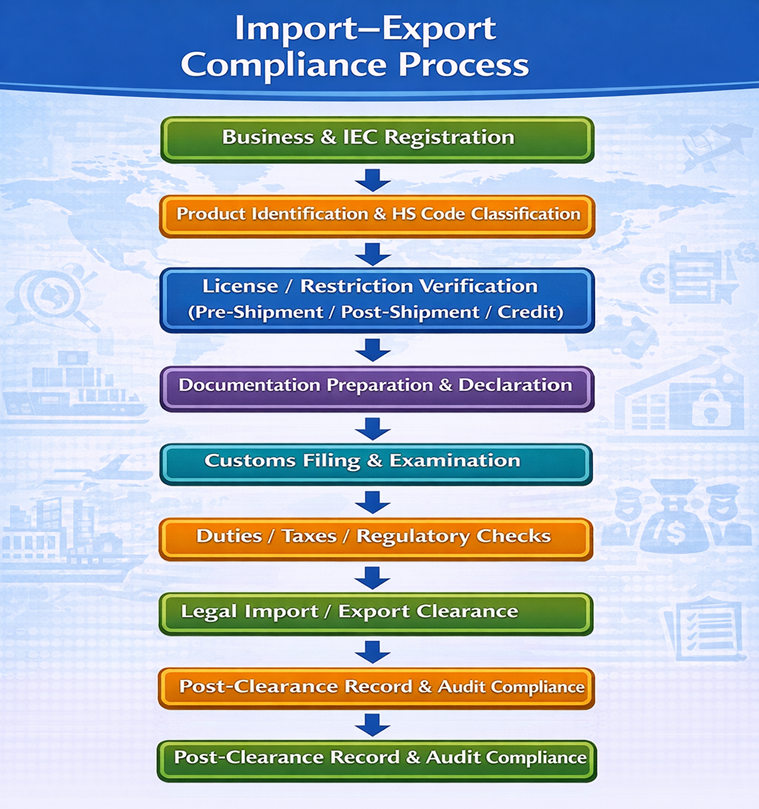
Conclusion
Import–Export Compliance is the foundation of sustainable international trade. Businesses that proactively manage compliance not only avoid penalties and delays but also gain financial, operational, and reputational advantages in global markets.
FAQs – Import–Export Compliance Requirements
Q1. What is import–export compliance? ▼
Import–export compliance refers to adhering to all laws, regulations, and documentation requirements governing international trade transactions.
Q2. Why is import–export compliance important for businesses? ▼
Compliance helps avoid penalties, shipment delays, cargo confiscation, and ensures smooth customs clearance and business continuity.
Q3. Which authorities regulate import–export compliance? ▼
Key authorities include Customs, DGFT, GST authorities, RBI, and other product-specific regulatory bodies.
Q4. What are the most common compliance mistakes? ▼
Common mistakes include incorrect HS code classification, wrong valuation, missing licenses, incomplete documentation, and delayed foreign exchange realization.
Q5. How does HS code impact import–export compliance? ▼
HS code determines customs duty, restrictions, licensing requirements, and eligibility for export incentives.
Q6. What documents are essential for import–export compliance? ▼
Key documents include commercial invoice, packing list, shipping bill or bill of entry, transport documents, and regulatory certificates.
Q7. How does foreign exchange regulation affect compliance? ▼
Exporters must comply with RBI and FEMA rules, including timely realization and proper reporting of export proceeds through banks.
Q8. What happens if a business fails to comply with trade regulations? ▼
Non-compliance can result in penalties, seizure of goods, suspension of IEC, audits, and legal action.
Q9. How can businesses improve their import–export compliance? ▼
Businesses can improve compliance by conducting regular audits, training staff, using digital tools, and consulting trade professionals.
Export Promotion Councils (EPCs)
What are Export Promotion Councils (EPCs)?
Export Promotion Councils (EPCs) are government-recognized, sector-specific organizations established to promote, develop, and regulate exports of particular product categories from India. These councils function under the Department of Commerce, Ministry of Commerce & Industry, and play a critical role in strengthening India’s global trade presence.
Each EPC represents a specific industry or product group, such as textiles, engineering goods, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, handicrafts, agricultural products, and services.
EPCs issue the Registration-Cum-Membership Certificate (RCMC), which is mandatory for exporters to claim benefits under DGFT export incentive schemes.
Key Functions of EPCs
- Product-wise export promotion
- Market intelligence & trade data
- Exporter representation to government
- Trade facilitation & compliance guidance
Why are Export Promotion Councils Important?
Export Promotion Councils act as a bridge between exporters and the government, ensuring that industry interests are protected while helping exporters grow internationally.
Key Importance of EPCs
-
Mandatory for Export Incentives
- RoDTEP
- Advance Authorization
- EPCG Scheme
- MEIS (legacy cases)
-
Market Development Support
- Participation in international trade fairs
- Buyer–seller meets
- Export promotion events & delegations
-
Policy Representation
- Representation to DGFT, Customs, and Ministry of Commerce
- Resolution of trade policy bottlenecks
-
Export Compliance Guidance
- Product standards
- Export documentation norms
- Quality certifications & testing requirements
Where are EPCs Used?
Export Promotion Councils are applicable across all export sectors and are essential at multiple stages of international trade.
Primary Areas of Use
- DGFT incentive claims
- Export documentation compliance
- Sector-specific export approvals
- International trade promotion activities
Sector-Wise Application Examples
| Sector | Export Promotion Council (EPC) |
|---|---|
| Engineering Goods | EEPC India |
| Textiles | TEXPROCIL |
| Chemicals | CHEMEXCIL |
| Pharmaceuticals | PHARMEXCIL |
| Handicrafts | EPCH |
| Agricultural Products | APEDA |
| Services | SEPC |
How to Register with Export Promotion Councils (EPCs)?
Every exporter must register with the relevant Export Promotion Council to obtain a Registration-Cum-Membership Certificate (RCMC), which validates the exporter’s eligibility for incentives and export benefits.
Step-by-Step EPC Registration Process
-
Step 1: Identify the Relevant EPC
Select the Export Promotion Council based on the primary export product HS code. -
Step 2: Online Application Submission
Apply through:- EPC website, or
- DGFT portal (for certain councils)
-
Step 3: Document Upload
Upload mandatory business and export documents. -
Step 4: Fee Payment
Pay applicable membership and registration fees. -
Step 5: Verification & Approval
EPC verifies the application and issues the RCMC. -
Step 6: Validity & Renewal
RCMC is generally valid for five years and must be renewed before expiry.
Documents Required for EPC Registration
- Import Export Code (IEC)
- PAN Card (Firm / Company)
- GST Registration Certificate
- Memorandum & Articles (Company) / Partnership Deed
- Bank Certificate / Cancelled Cheque
- Digital Signature Certificate (DSC)
- Product HS Code details
Flowchart – EPC Registration Process
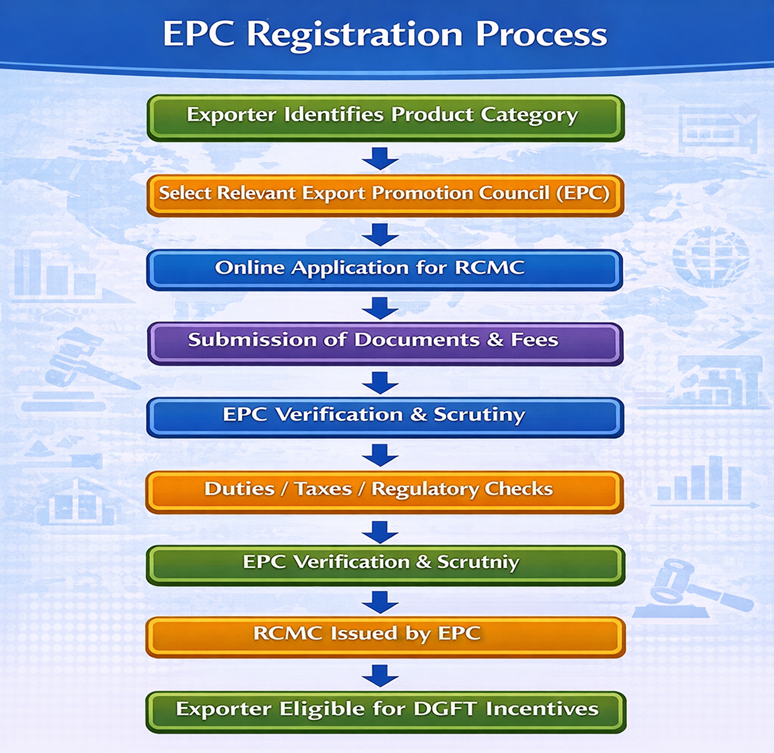
Key Benefits of EPC Membership
- Eligibility for export incentives
- Access to global market intelligence
- Trade fair participation support
- Policy advocacy & grievance redressal
- Training and capacity-building programs
Conclusion
Export Promotion Councils (EPCs) are a cornerstone of India’s export ecosystem. Registration with the appropriate EPC and obtaining an RCMC is not just a regulatory requirement—it is a strategic advantage that empowers exporters to expand globally, access incentives, and remain compliant.
FAQ – Export Promotion Councils (EPCs)
Q1. What is an Export Promotion Council (EPC)? ▼
An Export Promotion Council (EPC) is a government-recognized body that promotes and regulates exports of specific product or service sectors and supports exporters with incentives, market access, and compliance guidance.
Q2. Is EPC registration mandatory for exporters? ▼
Yes. EPC registration and RCMC are mandatory for exporters who wish to claim DGFT export incentives and benefits.
Q3. What is RCMC in export business? ▼
RCMC (Registration-Cum-Membership Certificate) is a certificate issued by an EPC confirming the exporter’s membership and eligibility for export incentive schemes.
Q4. How do I choose the correct EPC? ▼
The correct EPC is selected based on the primary HS code and nature of exported products or services.
Q5. What is the validity of an RCMC? ▼
RCMC is generally valid for five years and must be renewed before expiry to continue availing export benefits.
Q6. Can one exporter register with multiple EPCs? ▼
Yes, exporters dealing in multiple product categories may register with more than one EPC, subject to approval.
Q7. What documents are required for EPC registration? ▼
Key documents include IEC, PAN, GST certificate, bank details, business registration documents, and product HS codes.
Q8. What benefits do exporters get from EPC membership? ▼
Benefits include eligibility for incentives, trade fair participation, policy representation, market intelligence, and export training programs.
Q9. What happens if an exporter does not have an RCMC? ▼
Without an RCMC, exporters cannot claim DGFT incentives, may face delays in approvals, and miss EPC support services.
DGFT Schemes & Incentives
What is DGFT?
The Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) is the apex authority under the Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Government of India, responsible for formulating, implementing, and regulating India’s Foreign Trade Policy (FTP).
DGFT plays a central role in promoting exports, facilitating imports, and administering export incentive schemes that help Indian businesses compete globally.
Key Responsibilities of DGFT
- Issuance of Import Export Code (IEC)
- Administration of export incentive schemes
- Notification of Foreign Trade Policy (FTP)
- Authorization of restricted imports and exports
- Monitoring export obligations and compliance
Why DGFT Schemes Matter
DGFT schemes are designed to reduce the cost of exports, improve price competitiveness, and provide financial support to exporters.
Key Benefits of DGFT Schemes
-
Export Promotion
Encourages Indian manufacturers and service providers to expand into international markets. -
Cost and Tax Reduction
- Customs duties
- Embedded taxes
- Import duties on inputs
-
Global Competitiveness
Helps Indian products remain price-competitive against global suppliers. -
Liquidity Support
Provides duty credits or exemptions that improve cash flow and working capital.
Where are DGFT Schemes Applied?
DGFT schemes are applicable across multiple export channels and industries, covering goods, services, and modern digital trade models.
-
Merchandise Exports
- Manufacturing exports
- Trading exports
- Agricultural and industrial goods
-
Service Exports
- IT and ITES services
- Professional services
- Consulting, logistics, education, healthcare
-
E-Commerce Exports
- Cross-border online sales
- Small parcel exports
- Marketplace-based exports
Major DGFT Schemes & Incentives
-
RoDTEP (Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products)
- Refunds embedded taxes and duties
- Applicable to most tariff lines
- Issued as transferable duty credit scrips
-
Advance Authorization Scheme
- Duty-free import of inputs
- Linked to export obligation
- Ideal for manufacturers
-
EPCG (Export Promotion Capital Goods) Scheme
- Import of capital goods at zero or concessional duty
- Export obligation fulfilled over time
-
DFIA (Duty Free Import Authorization)
- Post-export duty-free input imports
- Used for standard input-output norms
-
Service Exports from India Scheme (SEIS – legacy)
- Incentives for eligible service exporters
- Applicable based on FTP notifications
How to Use DGFT Schemes & Incentives?
To successfully avail DGFT incentives, exporters must follow a structured, compliance-driven process aligned with the applicable Foreign Trade Policy.
-
Step 1: Obtain IEC Registration
IEC is mandatory for:- Exporting goods or services
- Filing DGFT applications
- Claiming incentives
-
Step 2: Identify Applicable DGFT Scheme
Selection depends on:- Product HS code
- Export category (goods or services)
- Nature of inputs and capital goods
-
Step 3: Ensure FTP Compliance
- Follow the current Foreign Trade Policy
- Adhere to scheme-specific conditions
- Meet export obligation timelines
-
Step 4: Execute Export Transaction
- Proper shipping bill declaration
- Correct scheme code selection
- Accurate documentation
-
Step 5: File DGFT Incentive Claim
- Online filing on DGFT portal
- Upload shipping bills, invoices, and eBRC
- Timely submission within prescribed limits
-
Step 6: Incentive Issuance & Utilization
- Duty credit scrip is issued
- Can be used for duty payment or transferred
Documents Required for DGFT Schemes
- Import Export Code (IEC)
- Shipping Bill (scheme declared)
- Commercial Invoice and Packing List
- eBRC / Bank Realization Certificate
- EPC / RCMC (where applicable)
- Chartered Accountant Certificate (if required)
Flowchart – DGFT Incentive Utilization Process
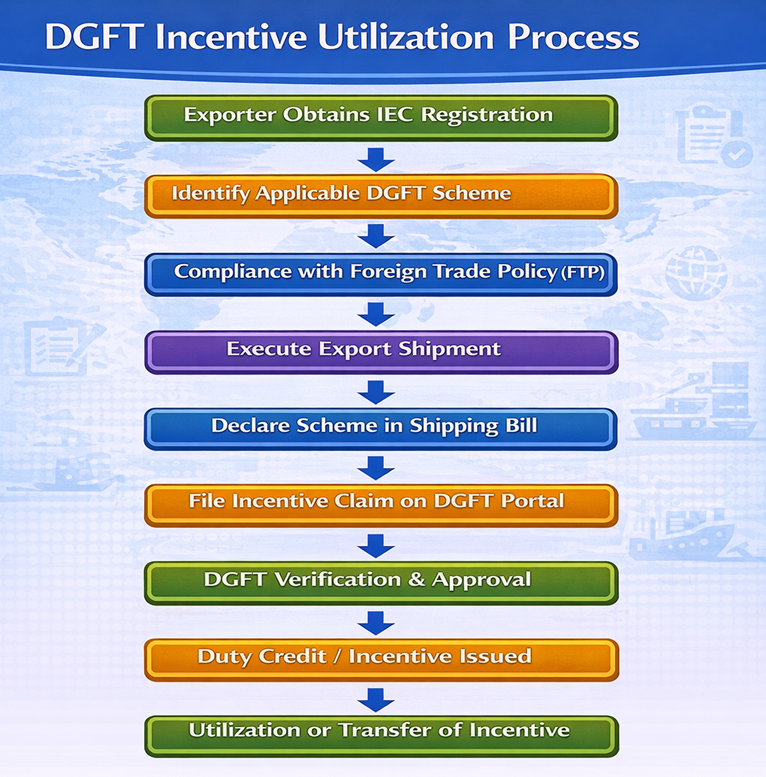
Common Challenges in DGFT Schemes
- Incorrect HS code declaration
- Missing scheme selection in shipping bill
- Delay in filing incentive claims
- Non-fulfillment of export obligations
- Frequent FTP policy changes
Conclusion
DGFT Schemes and Incentives form the backbone of India’s export promotion framework. When used correctly, they significantly reduce costs, improve profitability, and enhance global competitiveness. Successful utilization depends on accurate compliance, documentation, and timely filings.
FAQ – DGFT Schemes & Incentives
What are DGFT schemes? ▼
DGFT schemes are export incentive and facilitation programs introduced under India’s Foreign Trade Policy to promote exports and improve global competitiveness.
Who is eligible to avail DGFT export incentives? ▼
Any exporter with a valid IEC and compliance with FTP conditions is eligible, subject to scheme-specific criteria.
Which are the major DGFT incentive schemes? ▼
Major schemes include RoDTEP, Advance Authorization, EPCG, DFIA, and service export incentive schemes notified under FTP.
Is RCMC mandatory for DGFT incentive claims? ▼
Yes. RCMC from the relevant Export Promotion Council is mandatory for claiming most DGFT export incentives.
How are DGFT incentives received by exporters? ▼
DGFT incentives are generally issued as duty credit scrips, which can be used to pay customs duties or transferred.
What documents are required to claim DGFT incentives? ▼
Key documents include IEC, shipping bill, commercial invoice, eBRC, RCMC, and scheme-specific declarations.
What is the time limit to apply for DGFT incentives? ▼
Each scheme has a specific filing deadline. Late filing may lead to rejection or penalty.
Can DGFT incentives be transferred or sold? ▼
Most duty credit scrips are transferable, unless restricted under the applicable FTP or scheme conditions.
What are common reasons for rejection of DGFT claims? ▼
Common reasons include incorrect HS code, missing scheme declaration, incomplete documents, and non-compliance with export obligations.
International Trade Rules (WTO, FTAs & GATT)
What are International Trade Rules?
International Trade Rules are globally accepted legal frameworks that regulate cross-border trade of goods and services between countries. These rules aim to ensure fair competition, transparency, market access, and predictable trade conditions.
They govern key aspects such as:
- Customs duties and tariffs
- Import–export restrictions
- Trade remedies and safeguards
- Dispute settlement mechanisms
The most influential international trade frameworks include the World Trade Organization (WTO), General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), and Free Trade Agreements (FTAs).
Why are International Trade Rules Important?
International trade rules create a stable and rules-based trading system that benefits both developed and developing economies.
Key Importance of Trade Rules
-
Promote Free & Fair Trade
Prevent discriminatory trade practices and ensure equal treatment of member countries. -
Reduce Trade Barriers
Lower tariffs, remove quotas, and simplify customs procedures. -
Protect National Interests
Allow countries to safeguard domestic industries through anti-dumping and safeguard measures. -
Ensure Predictability
Businesses benefit from consistent rules, reducing uncertainty in international transactions.
World Trade Organization (WTO)
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is the primary global institution responsible for regulating international trade among member nations. It provides a common framework of rules that govern trade relations and ensures smooth functioning of global commerce.
WTO aims to promote free, fair, and predictable trade by reducing trade barriers and resolving disputes between countries.
Key Functions of WTO
- Administers global trade agreements
- Monitors national trade policies
- Resolves trade disputes between member countries
- Facilitates multilateral trade negotiations
WTO Agreements Cover
- Goods (GATT)
- Services (GATS)
- Intellectual Property (TRIPS)
General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT)
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is the foundation of modern international trade law. It was originally established to reduce tariffs and eliminate quantitative restrictions on trade in goods.
GATT forms the legal backbone of WTO rules related to trade in goods and ensures transparency and non-discrimination in global trade practices.
Core Principles of GATT
- Most Favoured Nation (MFN)
- National Treatment
- Tariff binding
- Transparency
Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)
Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) are bilateral or regional agreements between two or more countries that aim to provide preferential trade terms and improve market access among participating nations.
FTAs are designed to reduce trade barriers and encourage cross-border trade by offering advantages that are not available under general WTO rules.
Key Features of FTAs
- Reduced or zero customs duties
- Preferential market access
- Rules of origin requirements
- Mutual recognition of standards
Examples of FTAs
- ASEAN–India FTA
- India–UAE CEPA
- SAFTA
How Do International Trade Rules Impact Trade?
-
Preferential Tariff Benefits
Exporters can enjoy lower or zero import duties when trading under FTAs, improving price competitiveness in international markets. -
Rules of Origin Compliance
To claim FTA benefits, goods must meet origin criteria and be supported by valid Certificates of Origin (COO). -
Trade Remedy Measures
Countries can impose:- Anti-dumping duties
- Countervailing duties
- Safeguard measures
-
Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
WTO provides a structured dispute settlement system for resolving trade conflicts between nations.
Compliance Requirements under International Trade Rules
- Accurate HS code classification
- Certificate of Origin compliance
- Product standards and technical regulations
- Anti-dumping and safeguard awareness
- Documentation transparency
Flowchart – International Trade Rule Application Process

Challenges in Applying International Trade Rules
- Complex rules of origin
- Frequent policy changes
- Lack of awareness of FTA benefits
- Technical barriers to trade (TBTs)
- Dispute settlement delays
FTA vs WTO – Overview Comparison
| Basis | WTO (World Trade Organization) | FTA (Free Trade Agreement) |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Multilateral global trade framework | Bilateral or regional trade agreement |
| Coverage | All member countries globally | Limited to participating countries |
| Objective | Promote free, fair, and predictable global trade | Enhance trade between specific countries |
| Legal Status | Binding international treaty | Binding agreement between signatory nations |
| Trade Treatment | Non-discriminatory (MFN principle) | Preferential treatment for members |
| Tariff Reduction | Gradual, negotiated reductions | Immediate or phased duty reduction |
| Flexibility | Less flexible due to many members | Highly flexible and customized |
| Speed of Implementation | Slow due to multilateral consensus | Faster due to limited members |
Tariff & Market Access Comparison
| Aspect | WTO | FTA |
|---|---|---|
| Tariff Benefits | Standard MFN tariffs | Preferential or zero tariffs |
| Market Access | Equal access for all members | Enhanced access for partner countries |
| Quota Restrictions | Discouraged under WTO rules | Often removed or relaxed |
| Sensitive Products | Protected via negotiations | Negotiated exemptions may apply |
Compliance & Documentation Comparison
| Parameter | WTO | FTA |
|---|---|---|
| Rules of Origin | Not required | Mandatory |
| Certificate of Origin | Not applicable | Required to claim benefits |
| Product Standards | TBT & SPS disciplines | Mutual recognition may apply |
| Customs Procedures | Standardized | Simplified under agreement |
Dispute Resolution & Safeguards
| Criteria | WTO | FTA |
|---|---|---|
| Dispute Resolution | WTO Dispute Settlement Body | Joint committees / arbitration |
| Enforcement Strength | Strong multilateral enforcement | Limited to agreement terms |
| Safeguard Measures | Allowed under WTO rules | Often included with conditions |
| Anti-Dumping Rules | WTO governed | WTO-consistent provisions |
Business Impact Comparison
| Factor | WTO | FTA |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Savings | Moderate | High due to tariff elimination |
| Competitiveness | Baseline global access | Enhanced price advantage |
| Market Expansion | Global reach | Focused regional expansion |
| Compliance Complexity | Lower | Higher due to origin rules |
Conclusion
International Trade Rules under WTO, GATT, and FTAs form the legal foundation of global commerce. Understanding and correctly applying these rules allows businesses to reduce costs, access new markets, mitigate risks, and remain globally competitive.
FAQ – WTO, Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) & GATT
What is the World Trade Organization (WTO)? ▼
The WTO is a global trade body that regulates international trade, enforces trade agreements, and resolves disputes between member countries.
What is GATT and how is it related to WTO? ▼
GATT (General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade) is the foundational agreement governing trade in goods and forms the legal backbone of WTO trade rules.
What are Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)? ▼
FTAs are bilateral or regional trade agreements that offer preferential tariff benefits and improved market access between participating countries.
How do FTAs benefit exporters and importers? ▼
FTAs reduce or eliminate customs duties, making products more competitive and improving profitability in international markets.
What are Rules of Origin in FTAs? ▼
Rules of Origin define the criteria a product must meet to qualify for preferential tariff benefits under an FTA.
What is the Most Favoured Nation (MFN) principle? ▼
MFN requires WTO members to offer equal trade treatment to all member countries unless a specific FTA applies.
How are international trade disputes resolved? ▼
Trade disputes between countries are resolved through the WTO Dispute Settlement Mechanism, which provides binding rulings.
Can countries protect their domestic industries under WTO rules? ▼
Yes. WTO allows anti-dumping duties, countervailing duties, and safeguard measures to protect domestic industries from unfair trade practices.
Country-Specific Import Rules
What are Country-Specific Import Rules?
Country-Specific Import Rules are laws, regulations, and technical requirements imposed by an importing country to control the quality, safety, labeling, and eligibility of imported goods. These rules vary from country to country and are enforced to protect consumers, the environment, national security, and domestic industries.
Such regulations may include:
- Product standards and testing requirements
- Labeling and packaging rules
- Health, safety, and environmental norms
- Import licensing and certifications
- Pre-shipment inspections
Why are Country-Specific Import Rules Important?
Compliance with destination-country import rules is mandatory for market entry. Failure to comply can result in severe financial and operational consequences.
Key Importance
-
Market Access Authorization
Products are allowed entry only if they meet local regulatory standards. -
Avoidance of Rejections and Penalties
Non-compliance can lead to shipment rejection, cargo seizure, heavy fines, and blacklisting of exporters. -
Consumer and Environmental Protection
Ensures safety, quality, and sustainability standards are met. -
Reputation and Buyer Confidence
Consistent compliance builds trust with international buyers and regulatory authorities.
Where Do Country-Specific Import Rules Apply?
Country-specific import regulations are particularly strict in regulated industries and developed markets.
High-Risk and Highly Regulated Sectors
| Sector | Compliance Examples |
|---|---|
| Food & Agriculture | FDA (USA), EFSA (EU), phytosanitary rules |
| Pharmaceuticals | US FDA, EMA, GMP certification |
| Electronics | CE marking, FCC certification |
| Chemicals | REACH, RoHS |
| Textiles | Labeling, fiber content, safety norms |
Strict Import Markets
- United States
- European Union
- Japan
- United Kingdom
- Australia
- Canada
Types of Country-Specific Import Regulations
-
Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)
- Product standards
- Testing and certification requirements
- Packaging requirements
-
Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) Measures
- Food safety regulations
- Animal health standards
- Plant health and quarantine rules
-
Environmental and Safety Regulations
- Emissions and environmental standards
- Restrictions on hazardous substances
-
Labeling and Packaging Rules
- Language and translation requirements
- Country of origin marking
- Consumer information disclosure
How to Comply with Country-Specific Import Rules?
Exporters must follow a structured compliance process to meet destination-country import regulations and ensure smooth customs clearance.
-
Step 1: Identify Destination Country Regulations
Research applicable import laws through:- Official government portals
- Trade promotion bodies
- Importer or buyer guidance
-
Step 2: Classify Product Correctly
- Accurate HS code classification
- Determines applicable regulations and approvals
-
Step 3: Obtain Mandatory Certifications
Examples include:- CE, FDA, BIS, REACH, ISO
- Country-specific approvals
-
Step 4: Ensure Labeling and Packaging Compliance
- Language and measurement standards
- Safety warnings and disclosures
-
Step 5: Conduct Testing and Inspection
- Testing through accredited laboratories
- Pre-shipment inspection where required
-
Step 6: Prepare and Submit Import Documents
- Certificates and licenses
- Regulatory declarations
- Test reports and compliance documents
Common Challenges in Country-Specific Compliance
- Frequent regulatory changes
- Complex documentation requirements
- High certification and testing costs
- Lack of regulatory awareness
- Delays in testing and approvals
Flowchart – Country-Specific Import Compliance Process
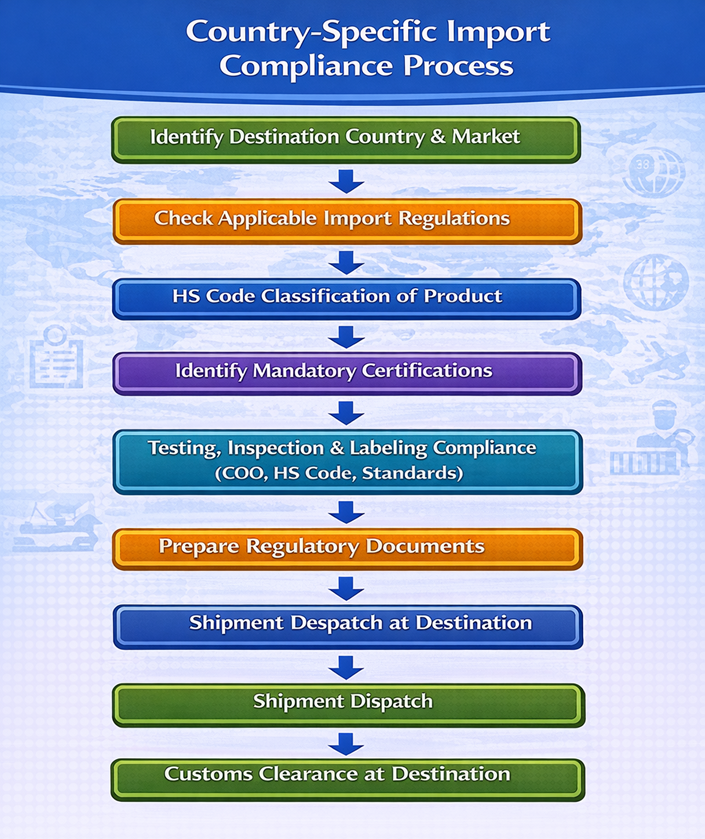
Best Practices for Exporters
- Engage local import agents or consultants
- Monitor regulatory updates regularly
- Maintain compliance checklists
- Conduct internal audits before shipment
Conclusion
Country-Specific Import Rules play a critical role in global trade compliance. Understanding and adhering to destination-country regulations ensures smooth market entry, reduced risk, and long-term international success.
FAQ – Country-Specific Import Rules
What are country-specific import rules? ▼
Country-specific import rules are regulations imposed by importing countries that define product standards, safety requirements, labeling, certifications, and import eligibility.
Why are country-specific import regulations important? ▼
They are mandatory for market access and help prevent shipment rejection, penalties, cargo seizure, and reputational damage.
How do import rules differ from country to country? ▼
Each country sets its own technical, safety, environmental, and labeling standards based on domestic laws and consumer protection needs.
Which products face the strictest import regulations? ▼
Highly regulated products include food, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, electronics, medical devices, and cosmetics.
What certifications are commonly required for imports? ▼
Common certifications include CE marking, FDA approval, REACH compliance, RoHS, BIS, and ISO standards, depending on the destination country.
How can exporters find applicable import regulations for a country? ▼
Exporters can refer to official government portals, customs websites, trade promotion bodies, and local import agents.
What happens if a shipment does not comply with import rules? ▼
Non-compliance can result in shipment rejection, re-export, destruction of goods, penalties, or importer blacklisting.
Are labeling requirements part of country-specific import rules? ▼
Yes. Most countries mandate specific labeling formats, language requirements, country-of-origin marking, and safety disclosures.
How can businesses ensure ongoing compliance with changing import regulations? ▼
By monitoring regulatory updates, maintaining compliance checklists, conducting audits, and consulting trade experts.
HS Code Master Guide
What is HS Code?
The HS Code (Harmonized System Code) is an internationally standardized numerical system developed by the World Customs Organization (WCO) for classifying traded products. It ensures uniform identification of goods across countries for customs clearance, duty assessment, and trade regulation.
HS Code Structure
- 2 digits: Chapter (product category)
- 4 digits: Heading (product group)
- 6 digits: Sub-heading (global standard)
- 8–10 digits: Country-specific tariff lines
Example:
HS Code 0902.30 – Black Tea (fermented)
Why is HS Code Critical in International Trade?
Accurate HS code classification is the foundation of import–export compliance and directly impacts cost, legality, and incentives.
Key Importance of HS Codes
-
Customs Duty Determination
HS code decides Basic Customs Duty (BCD), IGST, cess, and surcharges. -
Regulatory and Licensing Controls
Identifies whether a product is free, restricted, prohibited, or subject to licenses or certifications. -
Export Incentives and Benefits
HS code determines eligibility under DGFT schemes (RoDTEP, EPCG) and FTAs. -
Avoidance of Penalties
Incorrect HS code can lead to fines, shipment delays, incentive rejection, and legal disputes.
Where is HS Code Used?
HS codes are used throughout the entire international trade lifecycle.
Key Usage Areas
- Shipping Bill / Bill of Entry
- Customs clearance
- GST returns and duty calculations
- FTA claims and Certificates of Origin
- Trade statistics and government reporting
- Banking and trade finance documentation
How to Select the Correct HS Code?
Correct HS code selection requires a systematic, rule-based approach rather than guesswork or reliance on product names alone.
Step-by-Step HS Code Selection Process
-
Step 1: Analyze Product Composition
Understand:- Raw materials used
- Function and end use
- Manufacturing stage
- Degree of processing
-
Step 2: Identify the Relevant HS Chapter
Match the product with one of the 97 HS chapters based on its primary nature. -
Step 3: Select Correct Heading and Subheading
Use:- Section Notes
- Chapter Notes
- Heading descriptions
-
Step 4: Apply General Rules of Interpretation (GRI)
GRIs guide classification when multiple headings appear applicable. -
Step 5: Verify National Tariff Line
Check 8-digit (India) or 10-digit tariff lines for:- Applicable duty rates
- Import or export restrictions
- Eligibility for incentives
-
Step 6: Cross-Verify with Customs and Experts
Refer to:- Customs tariff schedules
- Customs Advance Ruling (if required)
- Trade consultants and CHAs
Where Do We Get HS Codes?
Official and Trusted Sources
- WCO Harmonized System Database
- National Customs Tariff (ICEGATE – India)
- DGFT ITC(HS) Schedule
- Customs Advance Ruling Authorities
- Trade consultants and Customs House Agents (CHAs)
General Rules of Interpretation (GRI) – Simplified
| GRI Rule | Purpose |
|---|---|
| GRI 1 | Classification based on heading text and section notes |
| GRI 2 | Covers incomplete, unfinished, or mixed goods |
| GRI 3 | Classification of composite and mixed goods |
| GRI 4 | Classification of similar products |
| GRI 5 | Classification of packaging and containers |
| GRI 6 | Determination of correct subheading |
HS Code Selection Process
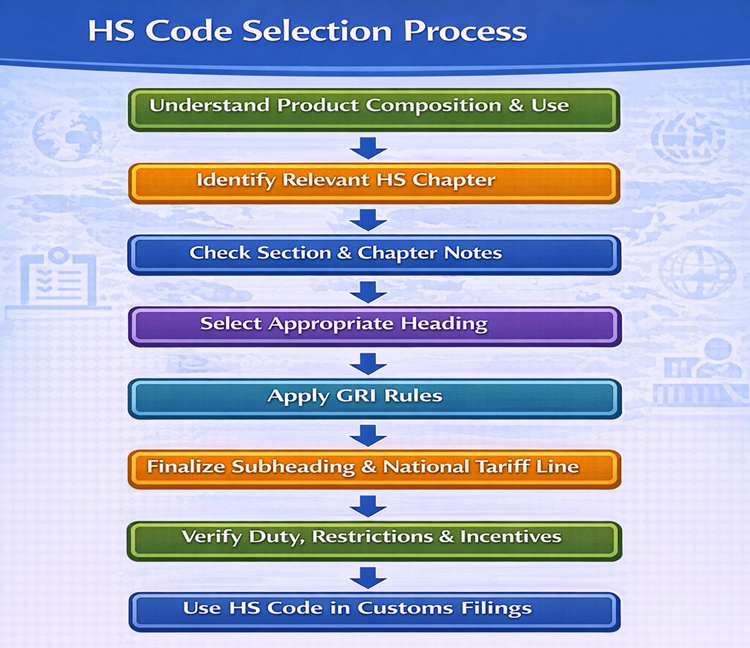
Best Practices for HS Code Accuracy
- Maintain product-wise HS code master
- Review HS codes periodically
- Seek advance ruling for complex products
- Train compliance and logistics teams
Conclusion
HS Code classification is the cornerstone of international trade compliance. Accurate selection ensures correct duty payment, incentive eligibility, regulatory compliance, and smooth customs clearance, while errors can lead to costly penalties and disputes.
FAQ – HS Codes (Harmonized System Codes)
What is an HS Code? ▼
An HS Code (Harmonized System Code) is a globally standardized numerical system used to classify traded products for customs, duty calculation, and trade regulation.
Who issues and maintains the HS Code system? ▼
The HS Code system is developed and maintained by the World Customs Organization (WCO) and adopted by over 200 countries.
Why is correct HS Code classification important? ▼
Correct HS code classification determines customs duties, regulatory requirements, export incentives, and compliance accuracy.
How many digits are there in an HS Code? ▼
HS Codes are standardized at 6 digits globally, while countries extend them to 8 or 10 digits for national tariff purposes.
Where can I find the correct HS Code for my product? ▼
HS Codes can be found through customs tariff schedules, DGFT ITC(HS), WCO databases, ICEGATE (India), and official customs portals.
What happens if an incorrect HS Code is used? ▼
Incorrect HS codes may lead to higher duties, penalties, shipment delays, incentive rejection, audits, and legal disputes.
Can the same product have different HS Codes in different countries? ▼
The first 6 digits remain the same globally, but the extended digits may vary based on country-specific tariff classifications.
What are the General Rules of Interpretation (GRI)? ▼
GRI are six legal rules used to resolve classification doubts and ensure consistent HS code selection.
How can businesses ensure long-term HS Code accuracy? ▼
By maintaining a product HS master database, conducting periodic reviews, seeking advance rulings, and training compliance teams.
Anti-Dumping, Sanctions & Trade Restrictions
What are Trade Restrictions?
Trade restrictions are regulatory measures imposed by governments or international bodies to control, limit, or regulate the import and export of goods, services, technology, or capital. These measures are designed to protect domestic industries, ensure national security, and enforce international law.
Trade restrictions typically include:
- Anti-dumping duties
- Countervailing duties
- Safeguard measures
- Economic and trade sanctions
- Export controls and embargoes
Why are Trade Restrictions Implemented?
Trade restrictions are introduced to correct market distortions and safeguard national interests.
Key Objectives
-
Prevent Unfair Pricing Practices
Anti-dumping measures counter below-cost pricing that harms domestic industries. -
Protect Strategic and Sensitive Goods
Controls export of dual-use items, defense equipment, and critical technologies. -
Enforce International Sanctions
Ensures compliance with UN, US, EU, and other international sanctions regimes. -
Maintain Economic Stability
Safeguards domestic markets during import surges or trade disruptions.
Key Types of Trade Restrictions
-
Anti-Dumping Duties
Anti-dumping duties are imposed when imported goods are sold at less than their normal value, causing material injury to domestic producers.- Requires investigation by designated authorities
- Time-bound but extendable after review
- Product and country specific
-
Countervailing Duties (CVD)
Countervailing duties are applied to neutralize subsidies provided by foreign governments to exporters, which distort fair competition. -
Safeguard Measures
Safeguard measures are temporary restrictions imposed to protect domestic industries from sudden and sharp import surges. -
Trade and Economic Sanctions
Sanctions are restrictions imposed against countries, entities, or individuals for political, security, or human rights reasons.
Types of Sanctions:- Comprehensive sanctions
- Sectoral sanctions
- Targeted sanctions (entity-based)
-
Export Controls and Embargoes
Export controls restrict the export of strategic, dual-use, or military goods to protect national security and foreign policy interests.
Where are Trade Restrictions Applied?
Trade restrictions are highly targeted and vary by product, country, and geopolitical considerations.
Common Applications
- Specific product categories such as steel, chemicals, and electronics
- Countries under international or unilateral sanctions
- Strategic industries including defense, energy, and telecommunications
Regulated Goods Examples
- Chemicals and hazardous materials
- Electronics and semiconductors
- Arms and defense equipment
- High-tech and dual-use items
How to Manage Risks of Trade Restrictions?
-
Continuous Policy Monitoring
- Track DGFT, Customs, and WTO notifications
- Monitor UN, US OFAC, and EU sanction updates
-
Country and Counterparty Risk Assessment
- Screen buyers, suppliers, and end-users
- Avoid sanctioned entities and jurisdictions
-
Product Classification and Licensing
- Correct HS code classification
- Verify export control classification numbers (ECCN)
-
Legal and Compliance Consultation
- Engage trade lawyers or compliance experts
- Obtain advance rulings or licenses where required
-
Robust Documentation and Record-Keeping
- Maintain licenses, approvals, and declarations
- Retain transaction records for audits
Consequences of Non-Compliance
- Heavy financial penalties
- Seizure of goods
- Criminal liability
- Loss of export privileges
- Reputational damage
Flowchart – Trade Restriction Compliance Process
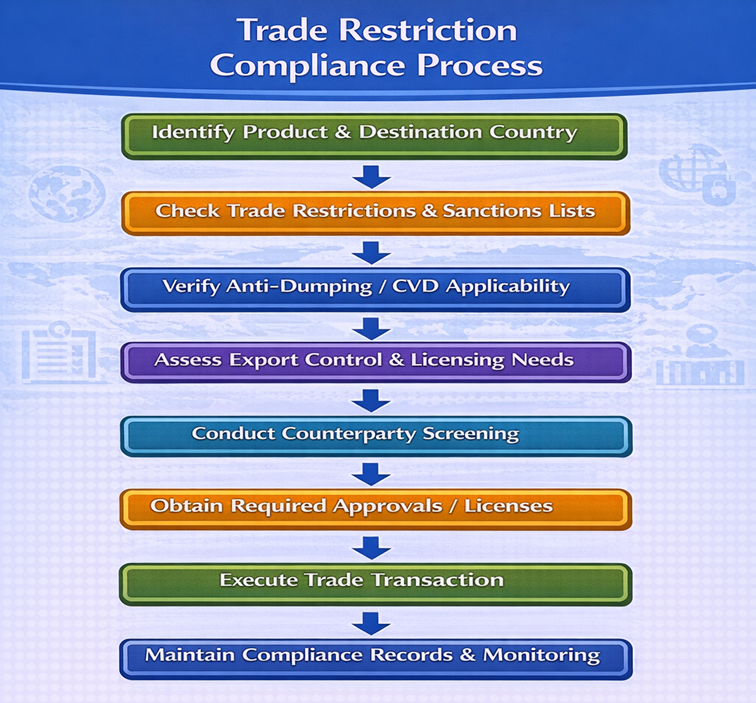
Best Practices for Businesses
- Implement compliance screening tools
- Train export and logistics teams
- Conduct periodic internal audits
- Maintain updated compliance checklists
Conclusion
Anti-dumping measures, sanctions, and trade restrictions are critical components of global trade governance. Businesses that proactively manage these risks through policy awareness, due diligence, and legal compliance can operate safely while avoiding costly penalties and disruptions.
FAQs – Trade Restrictions, Sanctions & Anti-Dumping Measures
What are trade restrictions in international trade? ▼
Trade restrictions are government-imposed controls on imports or exports to protect domestic industries, ensure national security, or comply with international agreements. These include anti-dumping duties, sanctions, export controls, quotas, and embargoes.
What is anti-dumping duty and when is it applied? ▼
Anti-dumping duty is imposed when imported goods are sold at below normal value, causing injury to domestic manufacturers. It is applied after a formal investigation and is product- and country-specific.
What is the difference between sanctions and trade restrictions? ▼
Trade restrictions broadly regulate trade flows, while sanctions are targeted measures imposed against specific countries, entities, or individuals for political, security, or legal reasons.
How do exporters know if their products are restricted? ▼
Exporters must check HS code-based notifications, DGFT and Customs circulars, WTO and country-specific trade rules, and international sanctions lists. Professional compliance screening is strongly recommended.
Which products are commonly subject to trade restrictions? ▼
Products frequently restricted include steel and chemicals, electronics and semiconductors, defense and dual-use items, pharmaceuticals, and hazardous goods. Restrictions vary by country and policy objectives.
What are export controls and why are they important? ▼
Export controls regulate the export of strategic, military, or dual-use goods to prevent misuse and protect national security. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties and criminal liability.
What happens if a company violates trade restriction laws? ▼
Violations may lead to heavy monetary penalties, seizure or destruction of goods, cancellation of export licenses, blacklisting, and legal prosecution.
How can businesses reduce trade restriction risks? ▼
Businesses should monitor trade policy updates, conduct country and buyer risk assessments, use compliance screening tools, and seek legal or trade compliance advice.
Are trade restrictions permanent? ▼
Most trade restrictions, including anti-dumping and safeguard duties, are time-bound but can be extended after review. Sanctions may change based on geopolitical developments and international negotiations.