Introduction to Ecommerce Exporting
What is Ecommerce Exporting?
Ecommerce exporting is the process of selling goods internationally through online channels, where a business located in one country supplies products directly to customers in foreign markets using digital platforms, online marketplaces, or brand-owned ecommerce websites.
Unlike traditional exports that rely heavily on distributors, agents, or physical overseas presence, cross-border ecommerce enables a direct-to-consumer (D2C) global trade model.
Ecommerce exporting is supported by:
- International logistics and fulfillment networks
- Cross-border payment gateways
- Export documentation and customs clearance systems
- Digital marketing and global customer acquisition tools
Ecommerce exporting integrates technology, logistics, compliance, and global demand into a single scalable business model.
Key Components of Ecommerce Exporting
- Digital storefront (online marketplace or brand-owned website)
- International customer base
- Cross-border logistics and shipping infrastructure
- Global payment collection and settlement systems
- Export compliance and international trade regulations
Why Ecommerce Exporting is Important for Global Businesses
-
Global Market Access Without Physical Presence
Businesses can sell products worldwide without opening overseas offices, warehouses, or retail stores, significantly reducing operational complexity. -
Low Entry Barriers and Cost Efficiency
- Lower capital investment
- No dependency on foreign distributors
- Minimal fixed operational costs
-
Faster Market Entry and Scalability
- Global product launch within days
- Quick market testing using real-time data
- Scalable expansion across multiple countries
-
Higher Profit Margins Through D2C Model
- Elimination of intermediaries
- Better pricing control
- Improved brand ownership and customer value
-
Data-Driven Global Decision Making
Ecommerce platforms provide insights into customer behavior, demand forecasting, and market-specific performance analytics.
When Should a Business Start Ecommerce Exporting?
Timing plays a critical role in ecommerce export success. A business should consider entering cross-border ecommerce when its product readiness, operational capability, and market opportunity align.
-
Domestic Market Saturation
Limited growth opportunities in the local market or intense competition that reduces margins often signal the right time to explore global customers. -
Global Demand for the Product
Products with universal or niche international appeal perform well in ecommerce exports, such as fashion, handicrafts, wellness products, electronics accessories, and lifestyle goods. -
Digital and Operational Readiness
- Ability to manage online orders
- Basic digital marketing capability
- Stable inventory and supply chain
-
Availability of Logistics and Payment Infrastructure
- Reliable international shipping partners
- Secure global payment gateways
- Export documentation readiness
-
Favorable Trade and Policy Environment
Export incentives, duty benefits, and simplified ecommerce export regulations significantly improve profitability and ease of operations.
Where Can Ecommerce Exporting Be Done?
Ecommerce exporting operates across multiple international regions and sales channels. Market selection depends on product demand, purchasing power, logistics accessibility, and regulatory ease.
Major Global Ecommerce Export Markets
- North America: United States, Canada
- Europe: United Kingdom, Germany, France, European Union nations
- Middle East: United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia
- Asia-Pacific: Singapore, Australia, Southeast Asia
How Ecommerce Exporting Works (End-to-End Process)
Ecommerce exporting follows a structured, technology-driven workflow that enables businesses to sell products internationally while complying with trade regulations, customs procedures, and customer expectations.
Step-by-Step Ecommerce Export Process
-
Product Identification and Compliance Check
Identify export-suitable products and verify compliance with destination-country regulations, quality standards, labeling rules, and certifications. -
International Market Research and Pricing Strategy
Analyze demand, competition, landed cost, customs duties, and logistics expenses to arrive at competitive global pricing. -
Ecommerce Platform or Website Onboarding
Register and onboard products on international marketplaces or brand-owned ecommerce websites with optimized listings and localized content. -
Export Registration and Documentation Setup
Complete export registrations such as IEC, banking arrangements, and prepare standard export documentation for ecommerce shipments. -
Order Placement by International Customer
Customers place orders through ecommerce platforms, triggering automated order processing, payment authorization, and shipping workflows. -
Pick, Pack and International Shipping
Products are picked, packaged as per international standards, and handed over to courier or logistics partners for cross-border transportation. -
Export and Import Customs Clearance
Shipments undergo export clearance in the origin country and import clearance in the destination country as per customs regulations. -
Global Delivery and Payment Settlement
Orders are delivered to international customers and payments are settled to the exporter’s bank account after deductions and reconciliation.
Flowchart – Ecommerce Export Overview
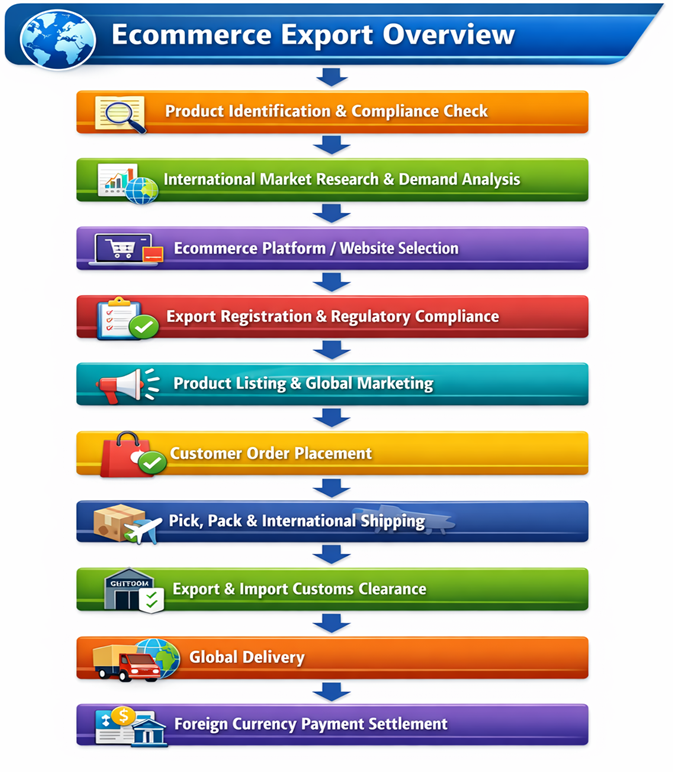
Strategic Importance of Ecommerce Exporting in Modern Trade
Ecommerce exporting is no longer optional—it has become a core driver of global trade transformation. Businesses that integrate ecommerce exports into their growth strategy gain long-term competitive advantages across markets.
- Global brand visibility without physical expansion
- Revenue diversification across multiple countries
- Risk mitigation through geographic market spread
- Scalable and sustainable international growth
With the integration of automation, data analytics, digital marketing, and smart logistics, ecommerce exporting is shaping the future of international trade.
Conclusion
Ecommerce exporting empowers businesses to access global markets with minimal entry barriers, faster execution, and direct customer relationships. By combining technology, logistics, and compliance into a unified model, businesses can scale internationally without traditional export complexities.
Companies that invest early in ecommerce export readiness build stronger global brands, unlock new revenue streams, and position themselves for long-term success in the evolving international trade ecosystem.
FAQs – Ecommerce Export Overview
What is ecommerce exporting? ▼
Ecommerce exporting is the process of selling products online to international customers using global ecommerce platforms or brand-owned websites, supported by cross-border logistics, international payments, and export compliance systems.
How does ecommerce exporting differ from traditional exporting? ▼
Traditional exporting relies on distributors and bulk shipments, whereas ecommerce exporting follows a direct-to-consumer model with individual order fulfillment, faster market entry, and better pricing control.
Who can start an ecommerce export business? ▼
Any manufacturer, trader, startup, MSME, or brand owner can start ecommerce exporting with an Import Export Code (IEC), compliant products, and reliable logistics and payment systems.
Which products are best suited for ecommerce exports? ▼
Products such as fashion and apparel, handicrafts, wellness products, electronics accessories, lifestyle items, and gift products perform well in ecommerce exports due to global demand and manageable logistics.
Which countries are popular for ecommerce exporting? ▼
Popular ecommerce export destinations include the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, European Union countries, the Middle East, Australia, and Southeast Asia.
What registrations are required for ecommerce exporting? ▼
Businesses typically require an Import Export Code (IEC), GST registration where applicable, an export bank account, and approvals from ecommerce marketplaces or website payment gateways.
How does logistics work in ecommerce exporting? ▼
Ecommerce export logistics includes order pickup, packaging, export customs clearance, international shipping, import clearance, and last-mile delivery, usually managed through courier or marketplace-integrated logistics partners.
How are payments received in ecommerce exports? ▼
Payments are received through international payment gateways or marketplace settlement systems and credited to the exporter’s bank account in compliance with foreign exchange and banking regulations.
Is ecommerce exporting profitable for small businesses? ▼
Yes. Ecommerce exporting offers low entry barriers, direct-to-consumer pricing, global demand access, and scalable operations, making it highly profitable for small and growing businesses.
Ecommerce Export Platforms
What are Ecommerce Export Platforms?
Ecommerce export platforms are digital ecosystems that enable businesses to sell products to international customers online. These platforms provide the technological and operational backbone required for cross-border ecommerce.
Ecommerce export platforms typically support:
- Global customer acquisition
- Online storefront and product listing
- Secure international payment processing
- Integrated logistics and fulfillment solutions
- Export documentation and compliance support
By eliminating the need for physical overseas presence, ecommerce export platforms allow exporters to scale globally with speed, efficiency, and reduced risk.
Types of Ecommerce Export Platforms
Ecommerce export platforms can be broadly classified into three categories. Each platform type serves different business objectives, investment capacities, and growth strategies.
-
Global Marketplaces
Large international marketplaces that connect sellers with buyers across multiple countries through a single platform. -
Regional Marketplaces
Platforms focused on specific geographic regions, offering localized customer access, payment methods, and logistics networks. -
Brand-Owned Ecommerce Websites
Seller-controlled ecommerce websites that enable direct-to-consumer international sales with full control over branding, pricing, and customer data.
Why Ecommerce Export Platform Selection Matters
Selecting the right ecommerce export platform is a strategic business decision that directly impacts sales growth, customer experience, operational efficiency, compliance, and long-term profitability.
-
Market Access and Global Reach
Ecommerce platforms provide instant access to millions of international buyers across multiple countries, reducing the time and cost required to enter new markets. -
Customer Trust and Brand Credibility
- Built-in customer trust mechanisms
- Verified seller programs
- Secure and recognized payment systems
Established platforms significantly improve conversion rates for new exporters.
-
Integrated Logistics and Payment Systems
- Cross-border shipping solutions
- Automated shipping labels and tracking
- Customs documentation support
- Multi-currency payment settlements
-
Compliance and Regulatory Assistance
- Restricted product checks
- Tax collection mechanisms
- Export documentation workflows
This reduces the compliance burden and risk for exporters.
-
Faster Go-to-Market
Sellers can begin exporting globally within days on ecommerce platforms, compared to months required in traditional export models.
When to Choose Which Ecommerce Export Platform
Different stages of business maturity require different ecommerce export platform strategies. The choice depends on resources, branding goals, and long-term expansion plans.
Marketplace Model – Ideal for Beginners and SMEs
Best suited when:
- Starting ecommerce exports for the first time
- Limited technical or digital marketing resources
- Immediate global visibility is required
Advantages:
- Ready-made international customer base
- Lower marketing effort
- Integrated logistics and payment systems
Brand-Owned Ecommerce Website – Ideal for Established Brands
Best suited when:
- Strong brand identity already exists
- Long-term global expansion is the goal
- Full control over pricing, data, and customer experience is required
Advantages:
- Complete ownership of customer data
- Higher profit margins
- Custom branding and marketing flexibility
Many successful exporters adopt a hybrid model, starting with marketplaces and gradually building brand-owned ecommerce websites.
How to Select the Right Ecommerce Export Platform
Selecting the right ecommerce export platform requires a structured, data-driven evaluation based on business goals, product characteristics, target markets, and operational capabilities.
Key Platform Selection Criteria
-
Product Category Compatibility
- Restricted versus non-restricted product status
- Demand for the product category on the platform
- Level of competition and price sensitivity
-
Target Country and Customer Behavior
- Local buying preferences
- Preferred payment methods
- Delivery speed and return expectations
-
Fee Structure and Cost Analysis
- Product listing and subscription fees
- Sales commission and referral fees
- Fulfillment and storage charges
- Currency conversion and settlement costs
-
Fulfillment and Logistics Options
- Platform-managed fulfillment solutions
- Seller-managed international shipping
- Cross-border return handling capabilities
-
Compliance and Tax Support
- Customs documentation assistance
- VAT or GST collection mechanisms
- Regulatory guidance for restricted markets
A well-selected ecommerce export platform minimizes operational risk, simplifies compliance, and significantly improves long-term profit margins.
Flowchart – Ecommerce Export Platform Selection Process
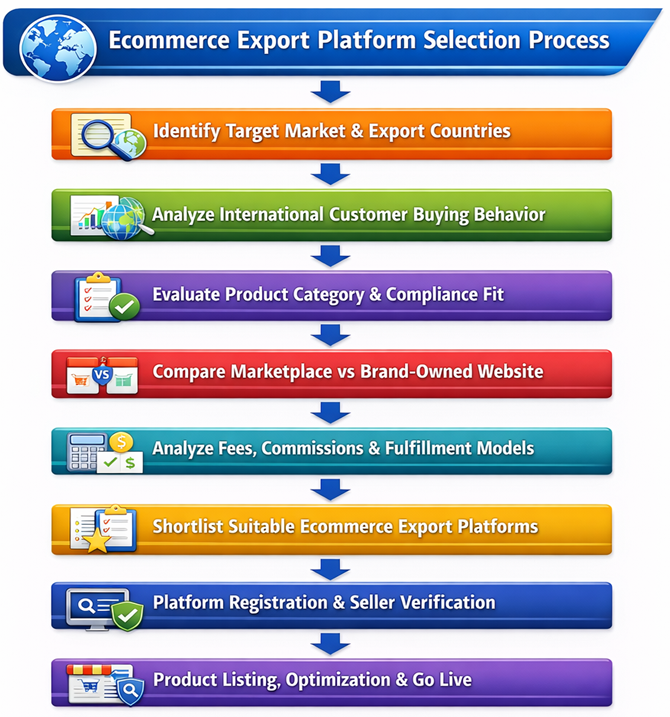
Strategic Role of Ecommerce Export Platforms in Global Trade
Ecommerce export platforms act as digital trade enablers, allowing businesses to participate in global commerce without the traditional barriers of physical presence, distributor dependence, or high capital investment.
- Enable rapid global market entry with minimal risk
- Provide instant access to international customers
- Support scalable logistics and fulfillment operations
- Simplify export compliance and tax management
- Help businesses build global brand visibility
In the evolving landscape of cross-border digital commerce, the right ecommerce export platform strategy determines long-term sustainability, profitability, and global competitiveness.
Conclusion
Ecommerce export platforms provide a powerful foundation for businesses seeking to expand internationally. By offering integrated technology, logistics, payment, and compliance support, these platforms reduce complexity and accelerate global growth.
Whether through global marketplaces, regional platforms, or brand-owned ecommerce websites, exporters who select the right platform mix can unlock sustainable revenue streams and build resilient international businesses.
FAQs – Ecommerce Export Platforms
What are ecommerce export platforms? ▼
Ecommerce export platforms are digital marketplaces or ecommerce systems that enable businesses to sell products to international customers by providing tools for product listing, global payments, cross-border logistics, and export compliance.
Which ecommerce export platforms are best for beginners? ▼
Global marketplaces such as Amazon Global, eBay, and Etsy are well suited for beginners and SMEs because they offer ready international customer bases, integrated logistics, secure payments, and built-in buyer trust.
What is the difference between marketplaces and brand-owned websites? ▼
Marketplaces provide faster global reach with lower setup effort, while brand-owned ecommerce websites offer full control over branding, pricing, customer data, and marketing. Many exporters adopt a hybrid approach.
Which countries can be targeted using ecommerce export platforms? ▼
Ecommerce export platforms enable sellers to target high-demand markets such as the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, European Union countries, the Middle East, Australia, and Southeast Asia.
How do payments work on ecommerce export platforms? ▼
Payments are processed through platform-integrated international payment gateways. Funds are credited to the exporter’s bank account after order confirmation, delivery, and platform settlement cycles.
Do ecommerce export platforms provide logistics support? ▼
Yes. Most platforms offer integrated logistics services including international shipping, customs documentation, tracking, last-mile delivery, and return management through courier or fulfillment partners.
What fees are charged by ecommerce export platforms? ▼
Fees may include product listing charges, sales commissions, fulfillment and storage costs, shipping fees, and currency conversion or payment gateway charges. Understanding the complete cost structure is critical for export pricing.
Are ecommerce export platforms compliant with trade regulations? ▼
Platforms provide basic compliance support, but exporters remain responsible for product compliance, HS code accuracy, and adherence to country-specific regulations. Professional compliance planning is recommended.
Can exporters use multiple ecommerce platforms simultaneously? ▼
Yes. Many exporters adopt a multi-platform strategy to diversify market risk, increase global visibility, and maximize sales across regions.
Ecommerce Registration Requirements
What are Ecommerce Registration Requirements?
Ecommerce registration requirements refer to the mandatory legal, tax, banking, and customs registrations that a business must obtain to export goods internationally through online platforms or brand-owned ecommerce websites.
These registrations ensure that ecommerce export transactions are:
- Legally recognized
- Tax-compliant
- Customs-cleared
- Eligible for foreign currency receipt
Without proper registration, ecommerce exporters may face shipment holds, payment delays, penalties, or cancellation of export benefits.
Why Ecommerce Registration is Mandatory
Ecommerce exports are governed by international trade laws, customs regulations, taxation frameworks, and foreign exchange rules. Proper registration is essential for seamless and compliant operations.
-
Legal Export Clearance
- Mandatory for filing export declarations
- Required for customs clearance at ports and courier terminals
-
Tax Benefits and Refund Eligibility
- Zero-rated tax treatment for exports
- GST refunds or exemptions where applicable
- Eligibility for input tax credit
-
Bank and Payment Gateway Approvals
- Receipt of foreign currency payments
- Compliance with foreign exchange regulations
- Export remittance reconciliation
-
Marketplace and Logistics Onboarding
- Mandatory seller verification by global marketplaces
- Eligibility for integrated logistics solutions
-
Avoidance of Penalties and Shipment Delays
- Prevents export violations
- Reduces risk of regulatory action
When Should Ecommerce Registration be Completed?
Ecommerce export registrations should be completed before a business begins listing products internationally or shipping goods to overseas customers. Early registration ensures uninterrupted operations and regulatory compliance.
Recommended Timing
- During initial business setup or export expansion planning
- Before onboarding on global ecommerce marketplaces
- Prior to accepting international orders or payments
Delaying ecommerce export registration can result in:
- Order cancellations by marketplaces
- Payment blockage or settlement delays
- Customs clearance failures
Where to Register for Ecommerce Exporting
Ecommerce exporters must interact with multiple regulatory, financial, and platform authorities depending on the type of registration required. Each authority plays a specific role in enabling compliant international trade.
Key Registration Authorities
- Government Export Authorities – Trade and customs departments responsible for export authorization and compliance
- Tax Departments – GST or VAT authorities for export tax treatment and refund processing
- Banks and Authorized Dealers – Foreign exchange compliance and export payment settlement
- Ecommerce Marketplaces – Seller verification and platform onboarding
Most ecommerce export registrations can now be completed online through official government and platform portals, improving transparency, speed, and efficiency.
How to Register for Ecommerce Exporting
The ecommerce export registration process is systematic and document-driven, designed to establish the exporter’s legal identity and ensure compliance with trade, tax, and foreign exchange regulations.
General Registration Process
-
Business Entity Formation
Register the business as a sole proprietorship, partnership, LLP, or company with valid legal identity and ownership structure. -
Online Application Submission
Apply for required export, tax, and banking registrations through official government or authorized portals. -
Upload of Required Documents
Submit business, identity, address, and banking documents as part of the registration process. -
Verification by Authorities
Relevant departments verify the submitted information and may request clarifications or additional documents. -
Issuance of Registration Certificates
Upon successful verification, registration certificates or codes are issued, enabling ecommerce export operations.
Common Documents Required
While documentation requirements may vary based on business structure and country, ecommerce exporters typically need the following documents:
- Business registration proof
- PAN or Tax Identification Number
- Registered address proof
- Bank account details and cancelled cheque
- Digital Signature Certificate (DSC)
Key Ecommerce Export Registrations Explained
Ecommerce exporting requires multiple registrations across trade, tax, banking, and customs authorities. Each registration serves a specific purpose in ensuring legally compliant and smooth international ecommerce operations.
1. Import Export Code (IEC)
What is IEC?
The Import Export Code (IEC) is a mandatory unique identification number issued by the
Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) for carrying out export and import activities.
Why IEC is Required
- Mandatory for customs clearance of export shipments
- Required for receipt of foreign currency payments
- Needed for onboarding on global ecommerce marketplaces
Applicability: One-time registration, valid for lifetime unless suspended or cancelled.
2. GST Registration (for Ecommerce Exports)
What is GST Registration?
GST registration enables ecommerce exporters to claim zero-rated export benefits,
tax refunds, and input tax credit where applicable.
Why GST is Important for Ecommerce Exporters
- Exports treated as zero-rated supply under GST law
- Eligibility for GST refunds on exported goods
- Mandatory for compliance with many ecommerce marketplaces
Note: Certain exporters may be exempt based on turnover limits, export structure, or prevailing government notifications.
3. Export Current Account
What is an Export Current Account?
A dedicated bank account used to receive international payments generated from
ecommerce export transactions.
Why It is Required
- Foreign currency settlement from overseas customers or marketplaces
- Monitoring and realization of export proceeds
- Bank reporting to regulatory authorities
Key Features: Linked with IEC and supports international remittances under foreign exchange regulations.
4. AD Code Registration (Authorized Dealer Code)
What is AD Code Registration?
AD Code registration links the exporter’s bank account with customs authorities,
enabling export payment tracking and reconciliation.
Why AD Code is Mandatory
- Generation of shipping bills for ecommerce exports
- Monitoring of export proceeds by customs and banks
- Processing of GST refunds related to exports
Where It is Registered: With customs authorities at the port, airport, or courier terminal of export.
Strategic Importance of Proper Ecommerce Registration
Proper ecommerce export registration forms the foundation of sustainable and scalable cross-border ecommerce operations. It ensures that exporters operate within legal frameworks while maximizing financial and operational efficiency.
- Builds credibility with customs, banks, and marketplaces
- Enables smooth export customs clearance
- Ensures timely receipt of international payments
- Unlocks eligibility for export incentives and tax benefits
- Reduces risk of penalties, shipment delays, and regulatory action
Flowchart – Ecommerce Export Registration Process
The flow below summarizes the sequential steps involved in completing ecommerce export registrations before starting international online sales.
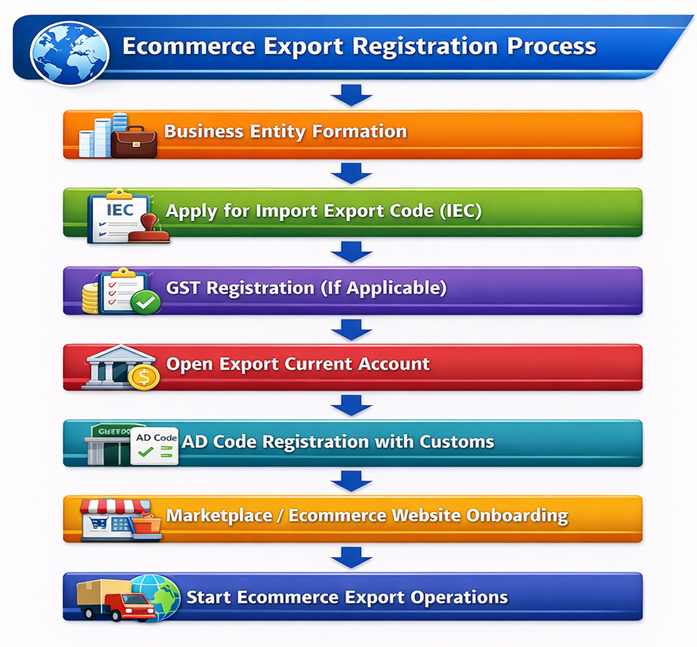
Conclusion
Ecommerce registration is not merely a compliance formality—it is a strategic enabler for global ecommerce success. Businesses that complete registrations correctly from the outset gain operational stability, financial transparency, and long-term scalability in international markets.
For exporters aiming to build reliable and compliant cross-border ecommerce operations, timely and accurate registration is the first and most critical step.
FAQs – Ecommerce Registration Requirements
What are ecommerce registration requirements for exports? ▼
Ecommerce registration requirements include legal, tax, banking, and customs registrations required to export goods online. These ensure lawful trade, smooth customs clearance, and foreign currency payment settlement.
Is Import Export Code (IEC) mandatory for ecommerce exports? ▼
Yes. IEC is mandatory for ecommerce exports and is required for customs clearance, receiving international payments, and onboarding on global ecommerce marketplaces.
Is GST registration required for ecommerce exporting? ▼
GST registration is generally required to claim zero-rated export benefits and tax refunds. Applicability may vary based on turnover, export structure, and prevailing government regulations.
Why is an export current account required? ▼
An export current account is required to receive foreign currency payments, comply with banking regulations, and enable monitoring of export proceeds.
What is AD Code registration and why is it important? ▼
AD Code registration links the exporter’s bank account with customs authorities, enabling shipping bill generation, export payment tracking, and tax refund processing.
When should ecommerce export registrations be completed? ▼
All ecommerce export registrations should be completed before listing products or shipping internationally to avoid payment blocks, shipment delays, or regulatory penalties.
Can individuals or small businesses register for ecommerce exports? ▼
Yes. Individuals, startups, MSMEs, and sole proprietors can register for ecommerce exports provided basic documentation and compliance requirements are met.
What happens if ecommerce export registrations are not completed? ▼
Without proper registration, exporters may face customs clearance rejection, payment settlement delays, loss of tax benefits, penalties, or shipment confiscation.
Ecommerce Logistics
What is Ecommerce Logistics?
Ecommerce logistics refers to the end-to-end movement and management of goods sold online from the seller to the international customer. It includes all operational activities required to ensure that products are stored, packed, shipped, customs-cleared, and delivered safely and on time across borders.
In the context of cross-border ecommerce, logistics extends beyond transportation and covers:
- Warehousing and inventory management
- Order fulfillment and export-grade packaging
- Export and import customs clearance
- International freight and courier services
- Last-mile delivery
- Returns and reverse logistics
Why Ecommerce Logistics is Critical for Exporters
-
Customer Satisfaction & Retention
Faster delivery times, accurate order fulfillment, and real-time shipment tracking improve customer trust and repeat purchases. -
Cost Optimization & Profitability
Optimized shipping routes, consolidated shipments, and efficient packaging reduce freight costs and return losses. -
Delivery Speed & Market Competitiveness
Shorter transit times increase conversion rates and help meet global customer expectations. -
Damage, Loss & Risk Reduction
Professional packaging, secure handling, and insurance coverage reduce transit damage and claims. -
Compliance & Smooth Customs Clearance
Accurate documentation, correct HS code classification, and regulatory adherence prevent shipment delays.
When Should Ecommerce Logistics Be Planned?
Ecommerce logistics must be planned before listing products for international sale. Early planning ensures cost control, regulatory compliance, and realistic delivery commitments.
Key Planning Stages
- Product design and export packaging stage
- Pricing and margin calculation
- Platform onboarding and product listing
Where Ecommerce Logistics Operations Occur
-
Seller Warehouse / Manufacturing Unit
Inventory storage, order picking, and primary packaging. -
Fulfillment Centers
Marketplace-managed or third-party facilities that enable automated packing, labeling, and faster dispatch. -
Export Customs Ports / Courier Terminals
Export declaration filing, customs inspection, and regulatory clearance. -
International Transit Hubs
Air cargo terminals, sea ports, and global logistics gateways. -
Import Customs & Last-Mile Delivery Hubs
Import clearance followed by local courier delivery to customers.
How Ecommerce Logistics Works (End-to-End Process)
Ecommerce logistics follows a systematic, technology-enabled workflow designed to ensure seamless cross-border delivery from the seller to the international customer. Each stage is interconnected and must be executed accurately to avoid delays, compliance issues, and customer dissatisfaction.
Step-by-Step Ecommerce Logistics Workflow
-
Order Received
The international customer places an order on an ecommerce marketplace or brand-owned website, triggering the fulfillment process. -
Pick & Pack
The product is picked from inventory and packed using export-grade packaging standards to ensure safety during international transit. -
Labeling & Documentation
Shipping labels are generated, and export documents such as the commercial invoice and packing list are prepared. -
Export Customs Clearance
Export declarations are filed with customs authorities, followed by document verification and regulatory clearance. -
International Transportation
The shipment is transported via air, sea, or express courier through global logistics networks. -
Import Customs Clearance
Import duties and taxes are assessed, and destination-country regulatory checks are completed. -
Last-Mile Delivery
The shipment is delivered by a local courier to the customer, followed by delivery confirmation.
Key Ecommerce Logistics Models
Ecommerce exporters can choose from different logistics models based on order volume, target markets, cost structure, and desired level of operational control. Selecting the right model is critical for delivery speed, customer satisfaction, and scalability.
1. Seller-Fulfilled Logistics
In seller-fulfilled logistics, the exporter manages inventory storage, order processing, packaging, and shipping independently or through courier partners.
Key Characteristics
- Full control over inventory and fulfillment operations
- Seller selects logistics and courier partners
- Suitable for low to medium order volumes
Best For
- Early-stage ecommerce exporters
- Niche or customized products
- Exporters prioritizing control over speed
2. Marketplace-Fulfilled Logistics
Marketplace-fulfilled logistics involves storing inventory at marketplace-managed fulfillment centers, where the platform handles packing, shipping, delivery, and customer returns.
Key Characteristics
- Platform-managed storage and fulfillment
- Faster delivery timelines
- Higher customer trust and conversion rates
Best For
- High-volume ecommerce exporters
- Fast-moving consumer goods
- Exporters targeting premium delivery standards
3. Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Third-party logistics providers offer end-to-end ecommerce logistics services, including warehousing, fulfillment, international shipping, and returns management.
Key Characteristics
- Outsourced logistics expertise
- Scalable and cost-efficient operations
- Technology-enabled inventory tracking
Best For
- Growing ecommerce exporters
- Multi-country or multi-platform sellers
- Businesses seeking operational efficiency
Strategic Role of Ecommerce Logistics in Global Trade
Ecommerce logistics is not merely an operational backend function. It is a strategic differentiator that directly influences market reach, customer experience, cost efficiency, and long-term competitiveness in cross-border ecommerce.
Exporters with well-structured logistics frameworks are able to deliver faster, operate more reliably, and scale internationally with reduced risk.
How Strong Logistics Creates Competitive Advantage
- Enables faster global market penetration
- Improves customer satisfaction and seller ratings
- Reduces shipping, handling, and return costs
- Minimizes customs delays and compliance risks
- Supports scalable growth across multiple countries
Flowchart – Ecommerce Logistics Process
The flowchart below illustrates the complete ecommerce logistics journey from order placement to international delivery, highlighting key operational and regulatory checkpoints.
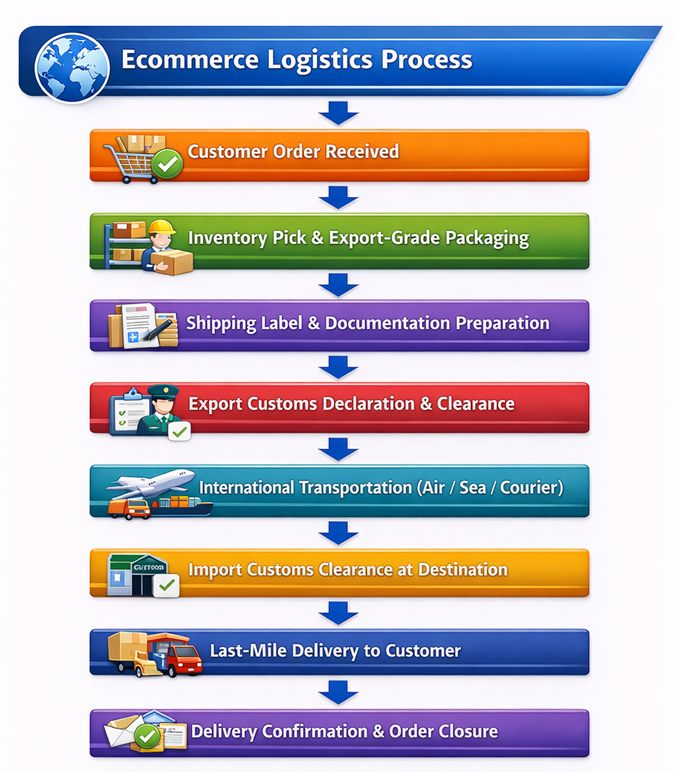
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) – Ecommerce Logistics
What is ecommerce logistics? ▼
Ecommerce logistics refers to the end-to-end movement of goods from an online seller to an international customer, including warehousing, order fulfillment, cross-border shipping, customs clearance, and last-mile delivery.
Why is ecommerce logistics important for international sellers? ▼
Ecommerce logistics directly impacts delivery speed, customer satisfaction, operational costs, and brand reputation. Efficient logistics ensures timely delivery, reduces damage and returns, and improves repeat purchases.
How does cross-border ecommerce shipping work? ▼
Cross-border ecommerce shipping follows a structured process: order confirmation, pick and pack, export customs clearance, international transit, import customs clearance, and last-mile delivery.
What logistics models are used in ecommerce exports? ▼
Common ecommerce logistics models include seller-fulfilled logistics, marketplace-fulfilled logistics, and third-party logistics (3PL). Each model differs in cost, control, scalability, and delivery speed.
When should ecommerce logistics planning be done? ▼
Ecommerce logistics should be planned before listing products for international sale. Early planning helps in accurate pricing, delivery time estimation, and regulatory compliance.
Where do ecommerce logistics operations take place? ▼
Ecommerce logistics operations span seller warehouses, fulfillment centers, export customs ports, international transit hubs, import customs facilities, and last-mile delivery centers.
What documents are required for ecommerce export logistics? ▼
Key documents include commercial invoice, packing list, shipping label, airway bill or courier receipt, and export declaration. Accurate documentation ensures smooth customs clearance.
How can ecommerce exporters reduce logistics costs? ▼
Logistics costs can be reduced by optimizing packaging, selecting the right fulfillment model, using consolidated shipping, and partnering with reliable logistics providers.
Does ecommerce logistics include returns and reverse logistics? ▼
Yes. Ecommerce logistics also includes reverse logistics, which covers international returns, replacements, refunds, and re-imports. Efficient reverse logistics improves customer satisfaction and inventory recovery.
Ecommerce Pricing & Profit Calculation
What is Ecommerce Export Pricing?
Ecommerce export pricing is the strategic process of determining the final selling price of products sold to international customers, taking into account all direct and indirect costs involved in cross-border ecommerce operations.
Unlike domestic pricing, international ecommerce pricing must account for additional variables such as:
- International logistics and freight charges
- Export and import duties
- Taxes and regulatory fees
- Ecommerce platform commissions
- Currency conversion and payment gateway costs
The objective of ecommerce export pricing is to achieve profitability, global competitiveness, and long-term business sustainability.
Why Pricing Accuracy is Essential in Ecommerce Exports
-
Profitability & Cost Recovery
Incorrect pricing can result in hidden losses due to underestimated logistics, taxes, or platform fees, directly impacting margins. -
Competitive Positioning in Global Markets
International customers compare prices across multiple sellers, countries, and ecommerce platforms. Accurate pricing improves conversion rates and market entry success. -
Avoidance of Financial Losses
Inaccurate pricing may lead to selling below cost, negative cash flow, and unsustainable business models. -
Strategic Decision Making
Proper pricing supports market expansion planning, product portfolio optimization, and promotion or discount strategy design.
When Should Ecommerce Export Pricing Be Calculated?
Ecommerce export pricing must be calculated before listing products on international marketplaces or ecommerce websites.
Key Pricing Touchpoints
- Product selection stage
- Marketplace or website onboarding
- Market entry planning
- Promotion and discount campaigns
Repricing may also be required when logistics costs change, currency exchange rates fluctuate, or ecommerce platform fee structures are updated.
Where Do Ecommerce Export Costs Arise?
-
Manufacturing / Product Cost
Raw material expenses, production costs, and quality control charges. -
Packaging & Handling Cost
Export-grade packaging, labeling, branding, and labor handling charges. -
Logistics & Freight Cost
Domestic pickup, international shipping by air, sea, or courier, and fuel surcharges. -
Customs Duties & Taxes
Import duties in destination countries, VAT, GST, sales tax, and customs processing fees. -
Ecommerce Platform Fees
Listing fees, sales commissions, fulfillment charges, and advertising or promotion costs. -
Financial & Transaction Costs
Currency conversion charges, payment gateway fees, and bank charges.
How to Calculate Ecommerce Export Price
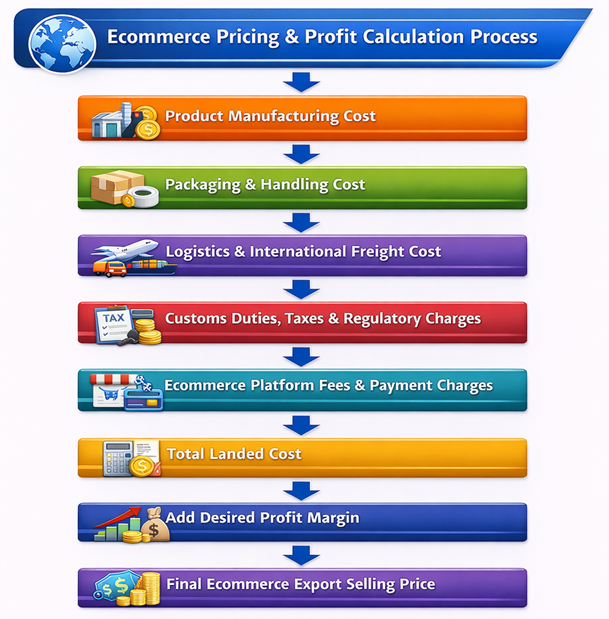
Ecommerce export pricing follows a landed-cost-based pricing approach. This method ensures that all direct and indirect costs are fully covered before adding the desired profit margin.
Standard Export Pricing Formula
Export Selling Price = Total Landed Cost + Desired Profit Margin
Step-by-Step Ecommerce Export Price Calculation
-
Calculate Product Cost
Include manufacturing cost, raw materials, labor, and quality control expenses associated with producing the product. -
Add Packaging & Handling Cost
Account for export-grade packaging, labeling, branding materials, and handling labor. -
Include Logistics & Freight Charges
Add domestic pickup, international shipping costs (air, sea, or courier), fuel surcharges, and insurance if applicable. -
Add Duties, Taxes & Regulatory Fees
Estimate import duties, VAT, GST, sales tax, and any customs processing or regulatory fees in the destination country. -
Include Platform & Payment Fees
Add ecommerce platform commissions, listing fees, fulfillment charges, payment gateway fees, and currency conversion costs. -
Determine Total Landed Cost
Sum up all cost components to arrive at the total landed cost per unit. -
Add Desired Profit Margin
Apply a profit margin based on market conditions, competition, and business objectives to determine the final selling price.
Profit Margin Considerations
Profit margins in ecommerce exports vary by product category, market competition, and brand positioning. Exporters should evaluate multiple factors before fixing margins.
- Level of market competition
- Product differentiation and uniqueness
- Brand positioning and perceived value
- Customer willingness to pay
Pricing Strategies Used in Ecommerce Exports
Ecommerce exporters use different pricing strategies depending on market competition, product type, brand positioning, and business objectives. Selecting the right pricing strategy is critical for profitability, scalability, and long-term success in global ecommerce.
1. Cost-Plus Pricing
Cost-plus pricing involves adding a fixed profit margin over the total landed cost of the product.
Key Characteristics
- Simple and easy to calculate
- Ensures cost recovery
- Lower pricing risk for new exporters
Best Suited For
- New ecommerce exporters
- Low-competition or niche products
- Businesses prioritizing margin safety
2. Market-Oriented Pricing
Market-oriented pricing is based on competitor pricing and prevailing market rates in the target country or platform.
Key Characteristics
- Price aligned with competitor benchmarks
- High sensitivity to market dynamics
- Focus on volume and competitiveness
Best Suited For
- Highly competitive ecommerce categories
- Price-sensitive international markets
- Fast-moving consumer products
3. Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing is determined by the perceived value of the product to the customer rather than the cost of production.
Key Characteristics
- Higher margins for differentiated products
- Strong emphasis on branding and quality
- Customer perception-driven pricing
Best Suited For
- Branded or premium products
- Unique or handcrafted goods
- Products with strong storytelling or differentiation
4. Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing involves adjusting prices in real time based on demand, seasonality, competitor actions, or algorithmic analysis.
Key Characteristics
- Data-driven and technology-enabled
- Responsive to market fluctuations
- Optimizes revenue and inventory movement
Best Suited For
- High-volume ecommerce exporters
- Seasonal or trend-driven products
- Businesses using AI or advanced analytics tools
Strategic Importance of Pricing in Global Ecommerce
Ecommerce pricing is not a one-time calculation. It is a continuous strategic process that directly influences profitability, competitiveness, and long-term sustainability in international markets.
Successful ecommerce exporters treat pricing as a dynamic business lever rather than a static number. Pricing decisions evolve with cost structures, market behavior, and competitive pressure.
How Strategic Pricing Drives Global Success
- Protects profit margins despite logistics and currency fluctuations
- Improves conversion rates through market-aligned pricing
- Enables controlled expansion into new international markets
- Supports effective promotion and discount strategies
- Ensures long-term business sustainability
Flowchart – Ecommerce Pricing & Profit Calculation Process
The flowchart below illustrates the complete ecommerce pricing workflow, from cost identification to final profit determination, highlighting the importance of landed-cost-based pricing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) – Ecommerce Pricing & Profit Calculation
What is ecommerce export pricing? ▼
Ecommerce export pricing is the process of setting the final selling price for products sold to international customers by considering product cost, international logistics, customs duties, taxes, platform fees, and profit margins.
Why is accurate pricing important in ecommerce exports? ▼
Accurate pricing ensures profitability, competitiveness, and sustainability. Incorrect pricing can lead to hidden losses, reduced margins, or uncompetitive pricing in global ecommerce markets.
When should ecommerce export pricing be calculated? ▼
Ecommerce export pricing should be calculated before listing products on international marketplaces or websites and reviewed regularly when costs, exchange rates, or platform fees change.
What costs should be included in ecommerce export pricing? ▼
Ecommerce export pricing should include manufacturing or product cost, packaging and handling, international logistics, customs duties and taxes, ecommerce platform commissions, and payment gateway or currency conversion fees.
How is ecommerce export profit calculated? ▼
Ecommerce export profit is calculated by subtracting the total landed cost from the final selling price. Profit equals selling price minus total cost.
What pricing strategies are used in ecommerce exports? ▼
Common ecommerce export pricing strategies include cost-plus pricing, market-oriented pricing, value-based pricing, and dynamic pricing. The choice depends on product type, competition, and target market behavior.
How do customs duties and taxes affect ecommerce export pricing? ▼
Customs duties and taxes increase the landed cost of a product. Accurate estimation of these costs is essential to avoid losses and maintain competitive pricing in destination markets.
How can ecommerce exporters improve profit margins? ▼
Exporters can improve margins by optimizing packaging and shipping costs, selecting the right ecommerce platforms, using data-driven pricing strategies, and negotiating better logistics rates.
Does currency exchange impact ecommerce export pricing? ▼
Yes. Currency exchange rate fluctuations directly affect selling prices and profit margins. Regular monitoring and timely price adjustments are necessary for sustainable ecommerce exports.
Ecommerce Documentation
What are Ecommerce Export Documents?
Ecommerce export documents are mandatory legal, commercial, and logistics records required to ship goods internationally, complete customs clearance, enable payment realization, and ensure regulatory compliance when selling products across borders through ecommerce platforms.
These documents act as proof of transaction, ownership, shipment, and export declaration in cross-border ecommerce.
Why Ecommerce Documentation is Important
- Enables smooth customs clearance at origin and destination
- Prevents shipment delays, penalties, or confiscation
- Supports foreign exchange realization and bank reporting
- Ensures compliance with export regulations and ecommerce policies
- Builds trust with logistics partners, marketplaces, and customers
Incorrect or missing documents are one of the most common reasons for ecommerce export shipment failure.
When are Ecommerce Export Documents Generated?
Ecommerce export documents are generated at multiple stages of the export transaction to ensure regulatory compliance and smooth shipment execution.
- After order confirmation on the ecommerce platform
- Before shipment dispatch from the seller or fulfillment center
- Before export customs filing
- Before handing over cargo to courier or freight forwarder
Timely document preparation ensures faster pickup, reduced customs queries, and on-time international delivery.
Where are Ecommerce Export Documents Used?
Ecommerce export documents are referenced and verified across multiple regulatory, financial, and operational checkpoints during cross-border trade.
-
Customs Authorities
- Export clearance processing
- HS code verification
- Duty, tax, and compliance checks
-
Banks & Payment Gateways
- Foreign currency realization
- Export proceeds reconciliation
- FEMA / RBI compliance reporting
-
Logistics & Courier Partners
- Shipment booking & routing
- Tracking and delivery confirmation
- Proof of export and transit documentation
-
Ecommerce Marketplaces
- Order validation and seller compliance
- Dispute resolution and claims handling
- Payment settlement verification
How Ecommerce Documentation Works
Ecommerce documentation follows a digital-first workflow that is tightly integrated with ecommerce platforms, courier systems, and customs portals.
- Order is confirmed on the ecommerce platform
- Commercial and logistics documents are generated
- Document data is shared with courier and customs systems
- Shipment is cleared and dispatched internationally
- Documents are archived for audits, refunds, and reconciliations
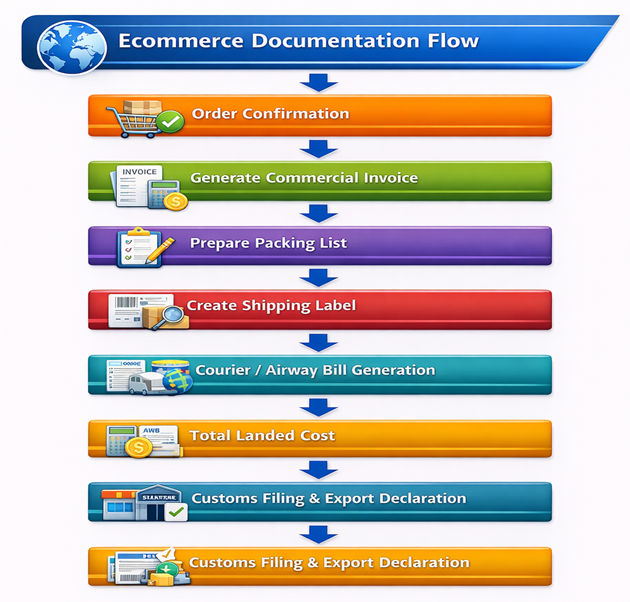
Key Ecommerce Export Documents
Ecommerce exports require a specific set of commercial, logistics, and customs documents. These documents collectively enable legal export clearance, international transportation, payment realization, and regulatory compliance.
1. Commercial Invoice
The commercial invoice is the primary legal document issued by the exporter to the overseas buyer. It forms the basis for customs valuation, duty calculation, and international payment settlement.
Key details included:
- Exporter and buyer details
- Product description and quantity
- HS code classification
- Invoice value and currency
- Incoterms
- Country of origin
2. Packing List
The packing list provides shipment-level packaging details and supports customs inspections and logistics handling.
Key details included:
- Number of packages
- Gross and net weight
- Package dimensions
- Type of packaging
3. Shipping Label
A shipping label is a barcode-based identification label attached to each parcel to enable automated routing, tracking, and delivery.
Key details included:
- Sender and receiver addresses
- Tracking number
- Service type
- Destination country code
4. Airway Bill (AWB) / Courier Receipt
The Airway Bill or courier receipt is issued by the logistics provider and serves as proof of shipment and contract of carriage.
Key functions:
- Proof of shipment dispatch
- Shipment tracking reference
- Carrier responsibility confirmation
5. Export Declaration (Shipping Bill / Courier Bill)
The export declaration is filed electronically with customs authorities and is mandatory for legal export clearance.
Key details included:
- Exporter IEC details
- Product classification and value
- Destination country
- Shipping and invoice references
Flowchart – Ecommerce Documentation Flow
Best Practices for Ecommerce Export Documentation
Implementing best practices in ecommerce documentation reduces compliance risk, prevents shipment delays, and improves operational efficiency.
- Use correct and consistent HS codes across all documents
- Maintain digital records of invoices, shipping bills, and airway bills
- Automate document generation through ecommerce platforms and courier systems
- Ensure invoice values match payment receipts and bank records
- Regularly audit documentation for regulatory and platform compliance
- Train operations teams on export documentation standards
Conclusion
Ecommerce documentation is the backbone of successful cross-border ecommerce operations. Every international ecommerce shipment depends on accurate, compliant, and timely documentation to move smoothly across borders.
Proper documentation ensures:
- Faster customs clearance at origin and destination
- Timely international delivery
- Smooth foreign currency payment realization
- Compliance with export regulations and ecommerce policies
- Reduced risk of penalties, delays, or shipment returns
For ecommerce exporters, a strong documentation process is not just a compliance requirement—it is a strategic enabler for scalability, customer satisfaction, and long-term global growth.
FAQs – Ecommerce Documentation
What is ecommerce export documentation? ▼
Ecommerce export documentation refers to the legal, commercial, and logistics documents required to ship products internationally, complete customs clearance, and receive foreign payments for cross-border ecommerce orders.
Why is documentation important in ecommerce exports? ▼
Proper documentation ensures smooth customs clearance, legal compliance, timely delivery, and payment realization. Incorrect or missing documents can cause shipment delays, penalties, or order cancellations.
When are ecommerce export documents generated? ▼
Ecommerce export documents are generated after order confirmation and before shipment dispatch to ensure compliance before customs filing and courier pickup.
What are the key documents required for ecommerce exports? ▼
Key ecommerce export documents include the commercial invoice, packing list, shipping label, airway bill or courier receipt, and export declaration.
Who uses ecommerce export documents? ▼
Ecommerce export documents are used by customs authorities, logistics and courier partners, banks and payment gateways, and ecommerce marketplaces for compliance and transaction verification.
Is digital documentation allowed in ecommerce exports? ▼
Yes. Most ecommerce exports use digital documentation such as e-invoices, electronic shipping bills, and digital airway bills, making the export process faster and more efficient.
What happens if ecommerce export documents are incorrect? ▼
Incorrect documentation can result in customs rejection, shipment delays, financial penalties, or return of goods, directly impacting exporter reputation and profitability.
How can ecommerce exporters manage documentation efficiently? ▼
Exporters can manage documentation efficiently by automating document generation, using compliant HS codes, maintaining digital records, and partnering with experienced logistics providers.
Ecommerce Import (Reverse Logistics)
What is Ecommerce Import / Reverse Logistics?
Ecommerce import or reverse logistics refers to the systematic process of managing international product returns, exchanges, refunds, repairs, and re-imports from overseas customers back to the seller or designated fulfillment centers.
In cross-border ecommerce, reverse logistics goes beyond simple returns and involves international transportation, customs clearance, inspection, inventory recovery, and financial reconciliation.
Why Reverse Logistics Matters in Ecommerce
An efficient reverse logistics system is critical for maintaining trust and operational stability in international ecommerce.
- Enhances customer satisfaction and buyer confidence
- Protects brand reputation in global markets
- Enables inventory recovery and resale opportunities
- Reduces financial losses from returns and refunds
- Ensures compliance with marketplace return policies
Poorly managed reverse logistics can lead to negative reviews, higher operational costs, customer churn, and regulatory complications.
When Does Reverse Logistics Occur?
Reverse logistics in ecommerce is triggered when an international order cannot be successfully completed or when a post-delivery issue arises.
- Customers request product returns or refunds
- Products arrive damaged, defective, or non-functional
- Incorrect items or quantities are delivered
- Customers initiate exchange or replacement requests
- Shipments are undeliverable or rejected at destination
Where Do Returned Ecommerce Goods Go?
Depending on cost, speed, and operational strategy, returned ecommerce goods can be routed to different locations for processing and recovery.
-
Seller’s Home-Country Warehouse
- Detailed inspection and quality assessment
- Repair, refurbishment, or repackaging
- Restocking, liquidation, or disposal
-
Local Fulfillment Centers (Destination Country)
- Faster return handling and resolution
- Lower reverse shipping costs
- Consolidated return shipments
-
Third-Party Reverse Logistics Providers
- Automated return processing
- Compliance and documentation support
- Inventory tracking and reporting
How Ecommerce Reverse Logistics Works
Ecommerce reverse logistics follows a structured, multi-stage international workflow involving customers, marketplaces, logistics partners, and customs authorities.
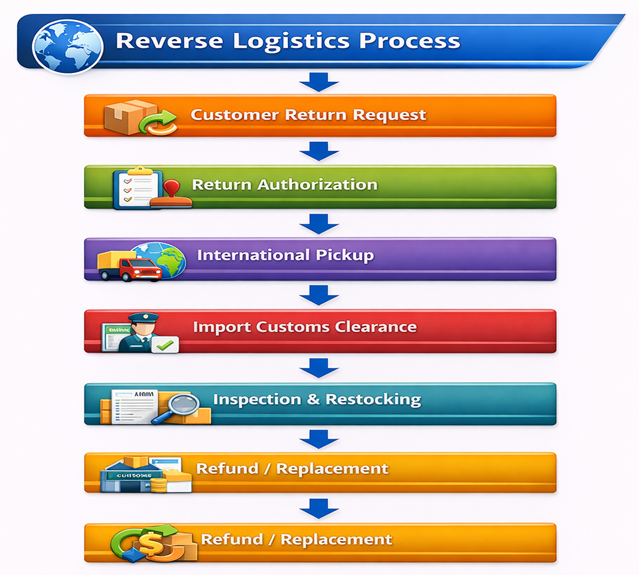
Step-by-Step Reverse Logistics Workflow
- Customer raises a return or refund request
- Seller reviews the request and issues Return Authorization (RA)
- International pickup and reverse shipment is arranged
- Goods pass through export and import customs clearance
- Returned shipment is received and inspected
- Refund, replacement, or exchange is completed
Key Components of Ecommerce Reverse Logistics
1. Return Authorization (RA)
Return Authorization is a formal approval issued by the seller or marketplace that allows the customer to return a product. It helps control unauthorized returns and enables tracking throughout the reverse logistics process.
2. International Pickup & Transportation
This stage involves arranging reverse shipping through international courier or logistics partners, including pickup scheduling, tracking, and reverse shipping label generation.
3. Import Customs Clearance
Returned goods must undergo import customs clearance in the destination country. This requires accurate re-import documentation, valuation assessment, and compliance with local import regulations.
4. Inspection & Quality Check
Upon receipt, returned items are inspected to determine their condition and eligibility for resale, repair, refurbishment, or disposal.
- Damage assessment
- Resale eligibility evaluation
- Repair or disposal decision
5. Refund, Replacement, or Exchange
The final resolution is completed based on the seller’s return policy, marketplace guidelines, and the condition of the returned product.
Compliance Considerations in Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics in cross-border ecommerce is subject to import regulations, customs valuation rules, tax laws, and marketplace compliance requirements. Failure to comply can result in financial losses or shipment rejection.
- Accurate re-import declaration with customs authorities
- Proper valuation of returned goods to avoid double taxation
- Eligibility assessment for refund of import duties and taxes
- Compliance with marketplace return and refund policies
- Maintenance of return documentation for audits
Flowchart – Reverse Logistics Process
Best Practices for Ecommerce Reverse Logistics
A well-designed reverse logistics strategy minimizes losses, improves customer experience, and ensures compliance in cross-border ecommerce operations.
- Define clear and transparent international return policies
- Use local or regional return centers to reduce shipping costs
- Automate return tracking, approvals, and documentation
- Partner with experienced reverse logistics service providers
- Analyze return data to identify product or process issues
- Align reverse logistics workflows with marketplace policies
Conclusion
Ecommerce import and reverse logistics play a vital role in building a reliable and scalable global ecommerce business. As international ecommerce grows, effective management of returns, exchanges, and re-imports becomes essential.
A structured reverse logistics system helps businesses:
- Maintain customer trust and satisfaction
- Recover inventory value efficiently
- Reduce operational and financial losses
- Ensure compliance with customs and marketplace rules
- Improve long-term global brand reputation
Reverse logistics is no longer just a cost center. When managed strategically, it becomes a competitive advantage in international ecommerce.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) – Ecommerce Import (Reverse Logistics)
What is ecommerce import or reverse logistics? ▼
Ecommerce import or reverse logistics refers to the management of international product returns, exchanges, refunds, and re-imports from overseas customers back to the seller or fulfillment center.
Why is reverse logistics important in ecommerce exports? ▼
Reverse logistics is important to maintain customer satisfaction, protect brand reputation, recover inventory value, and comply with marketplace return policies in global ecommerce.
When does reverse logistics occur in ecommerce? ▼
Reverse logistics occurs when customers request returns, replacements, refunds, or exchanges, or when shipments are undelivered, damaged, or rejected.
Where do returned ecommerce products go? ▼
Returned products may go to the seller’s warehouse, local fulfillment centers, or third-party reverse logistics hubs, depending on cost, speed, and return policy.
How does cross-border reverse logistics work? ▼
The process involves return authorization, international pickup, import customs clearance, inspection, and final resolution such as refund or replacement.
Do returned ecommerce goods require import customs clearance? ▼
Yes, international returns usually require import customs clearance, proper documentation, and compliance with re-import regulations of the destination country.
How can ecommerce exporters reduce reverse logistics costs? ▼
Costs can be reduced by:
- Using local return centers
- Improving product quality and descriptions
- Offering partial refunds
- Partnering with reverse logistics specialists
What challenges exist in ecommerce reverse logistics? ▼
Common challenges include high shipping costs, customs delays, duty recovery issues, and inventory damage, especially in cross-border returns.
How can technology improve ecommerce reverse logistics? ▼
Technology helps by enabling automated return approvals, real-time tracking, digital documentation, and return data analytics for better decision-making.