International Finance
Understanding Letters of Credit (LC)
What is a letter of credit (LC)?
A Letter of Credit (LC) is a formal financial instrument issued by a bank that guarantees payment to an exporter on the fulfillment of specific terms and conditions. It acts as a secure payment mechanism in international trade, ensuring that exporters receive payment even if the buyer defaults. LCs are particularly crucial in cross-border transactions where trust between new or unfamiliar trading partners may be limited.
There are several types of LCs used in international trade, including:
- Revocable LC – Can be altered by the issuing bank without the exporter’s consent.
- Irrevocable LC – Cannot be changed without agreement from all parties; the most commonly used in trade.
- Confirmed LC – A second bank (usually in the exporter’s country) guarantees payment in addition to the issuing bank.
- Sight LC – Payment is made immediately upon presentation of compliant documents.
- Usance or Deferred LC – Payment is made after a specified period, allowing buyers time to pay.
Why use a letter of credit?
1. Payment Security:
An LC ensures that the exporter receives payment once all the stipulated terms are met, eliminating the risk of non-payment from buyers. This is especially vital in high-value international shipments.
2. Risk Mitigation:
LCs reduce commercial and political risks. Commercial risks include buyer insolvency or refusal to pay, while political risks include currency restrictions, war, or government interventions in the buyer’s country.
3. Builds Trust in International Trade:
By using an LC, exporters and importers can conduct business without needing a long-standing relationship, facilitating cross-border trade expansion.
4. Facilitates Financing:
Exporters can use an LC as a collateral document to obtain pre-shipment or post-shipment finance from banks, improving cash flow.
Where is a letter of credit used?
- International Trade Transactions: LCs are most commonly used in import-export operations where buyers and sellers are in different countries.
- High-Value Transactions: For expensive machinery, bulk commodities, or technology exports, LCs provide assurance of payment.
- Emerging Markets or High-Risk Countries: LCs mitigate payment uncertainties in countries with volatile economies, political instability, or weak legal systems.
How does a letter of credit work?
- Agreement Between Buyer and Seller
- LC Request to Issuing Bank
- LC Advising and Notification
- Shipment of Goods
- Document Submission and Verification
- Payment Release
- Settlement and Delivery
Key advantages of letters of credit (LC) in international trade
| Advantage | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Secure Payment | Bank guarantee ensures exporters are paid for compliant shipments. |
| Risk Reduction | Minimizes buyer default and political risk. |
| Financing Facility | Can be used to obtain pre-shipment or post-shipment loans. |
| Trust Building | Enables transactions with new or unfamiliar partners. |
| Legal Framework | Governed by UCP 600 (Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits), providing standardized rules. |
Case Study: Letters of Credit (LC) – Advanced Insights
Overview of the Case Study
This case study examines the process of obtaining and releasing a Letter of Credit (LC) in international trade, highlighting common challenges, required documentation, and best practices for exporters and importers. It is based on real-world scenarios, providing practical knowledge for global business transactions.
LC Release Process – Step by Step
1. Agreement Between Buyer and Seller
- Buyer and seller finalize the sales contract, agreeing to use an LC for payment.
- Contract specifies type of LC (sight, usance, confirmed, revocable/irrevocable), shipment terms, and required documents.
2. Buyer Requests LC from Issuing Bank
- Buyer applies to their bank (issuing bank) to open LC.
- Bank assesses buyer creditworthiness and available limits.
3. Issuing Bank Issues LC
- LC is issued in favor of the exporter and sent to the exporter’s bank (advising bank).
- Advising bank authenticates the LC and notifies the exporter.
4. Exporter Ships Goods & Prepares Documents
- Exporter ships goods as per contract and collects mandatory documents.
- Documents include invoice, packing list, bill of lading, insurance certificate, and LC-specific certificates.
5. Document Submission to Advising Bank
- Exporter submits documents to advising bank.
- Bank checks compliance and forwards documents to issuing bank.
6. Issuing Bank Verification & Payment Release
- Issuing bank reviews documents.
- Sight LC: Payment immediately upon verification.
- Usance/Deferred LC: Payment at agreed future date.
7. Buyer Receives Documents & Clears Goods
- Buyer collects documents from issuing bank.
- Goods are cleared and transaction is completed.
Common Problems in Obtaining an LC from Bank
1. Documentation Errors
- Mistakes in invoice, shipping documents, or certificates.
- Non-compliance with LC terms can delay or block payment.
2. Bank Delays
- Slow verification by issuing or advising bank may affect shipment schedules.
3. Credit Limit Issues
- Buyer’s bank may reject or limit LC due to insufficient credit or collateral.
4. Type of LC Complexity
- Revocable LC: Risk of modification without exporter consent.
- Confirmed LC: Requires coordination between two banks.
- Usance LC: Payment delayed; exporter may face cash flow constraints.
5. Political or Regulatory Risks
- Changes in government regulations, currency controls, or sanctions may impact LC issuance or payment.
Required Documents for LC
A. From Exporter (Seller) to Bank:
- Commercial Invoice – Detailed description of goods.
- Packing List – Quantity, weight, and packaging details.
- Bill of Lading / Airway Bill – Proof of shipment.
- Insurance Certificate – Required if goods are insured.
- Certificate of Origin – Specifies country of manufacture.
- Inspection Certificate (if required) – Verifies quality/quantity.
- Other LC-specific Documents – Per LC terms (e.g., phytosanitary, fumigation certificates).
B. From Buyer to Bank:
- LC application form with buyer details, LC amount, currency, and terms.
- Sales Contract – Agreement with exporter.
- Proof of fund availability or collateral (for bank approval).
Considerations According to LC Type
| LC Type | Key Considerations for Buyer | Key Considerations for Seller |
|---|---|---|
| Sight LC | Payment made immediately after document verification. Ensure funds are available. | Prepare documents accurately to avoid payment delays. |
| Usance/Deferred LC | Cash flow planning is essential. | Understand credit period and risk of delayed payment. |
| Confirmed LC | Reduces risk if issuing bank is in unstable country. | Verify confirming bank’s reliability; payment guaranteed. |
| Revocable LC | Flexible but risky; bank can amend terms without consent. | Avoid unless in trusted trade relationship. |
| Irrevocable LC | Most secure; cannot be modified without agreement. | Ensure all document conditions are strictly met. |
Practical Tips for Smooth LC Transactions
- Detailed Contract: Clearly mention LC type, terms, and required documents.
- Early Bank Consultation: Engage both issuing and advising banks before shipment.
- Document Accuracy: Cross-check all documents to match LC terms exactly.
- Use Confirmed LC for High-Risk Markets: Provides extra security for exporters.
- Plan for Cash Flow in Usance LC: Prepare for deferred payment scenarios.
- Monitor Political and Regulatory Risks: Stay updated on import/export regulations in buyer country.
LC Release Process Flowchart
FAQ – Understanding Letters of Credit (LC)
Q1. What is a Letter of Credit (LC) in international trade? ▶
A Letter of Credit (LC) is a bank-issued financial guarantee that assures an exporter (seller) of payment once all specified terms and documentary conditions are fulfilled. It is widely used in international trade finance to minimize payment and credit risks between buyers and sellers located in different countries.
Q2. Why is a Letter of Credit important for exporters? ▶
An LC protects exporters against buyer default, delayed payment, and country risks. Since payment is guaranteed by a bank, exporters receive funds as long as they present LC-compliant documents, regardless of the buyer’s financial condition.
Q3. Why do importers use Letters of Credit? ▶
Importers use LCs to ensure that payment is released only after shipment is completed and documents comply with agreed terms. This provides control over shipment quality, quantity, and timing while maintaining trust with foreign suppliers.
Q4. Who are the main parties involved in an LC transaction? ▶
The key parties involved in a Letter of Credit transaction include:
- Applicant: Importer / Buyer
- Issuing Bank: Buyer’s bank that issues the LC
- Beneficiary: Exporter / Seller
- Advising Bank: Exporter’s bank that advises the LC
- Confirming Bank (if applicable): Bank that adds payment guarantee
Q5. What documents are required under a Letter of Credit? ▶
Common LC documents include:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading / Airway Bill
- Insurance Certificate
- Certificate of Origin
- Inspection or Quality Certificate (if required)
- Any additional documents specified in the LC
All documents must strictly match LC terms to avoid discrepancies.
Q6. What is the LC release process? ▶
- Buyer applies for LC issuance
- Issuing bank issues LC
- Advising bank notifies exporter
- Exporter ships goods
- Documents submitted to bank
- Bank verifies compliance
- Payment released (Sight or Usance)
Q7. What is the difference between Sight LC and Usance LC? ▶
| Feature | Sight LC | Usance LC |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Timing | Immediate | Deferred |
| Cash Flow Impact | Faster for exporter | Credit period to buyer |
| Risk Level | Lower | Slightly higher |
Q8. What is an Irrevocable Letter of Credit? ▶
An Irrevocable LC cannot be amended or canceled without the consent of all parties involved. It is the most commonly used LC in international trade due to its high level of security.
Q9. What is a Confirmed Letter of Credit? ▶
A Confirmed LC includes an additional payment guarantee from a second bank, usually in the exporter’s country. It protects exporters from issuing bank failure or political risks in the buyer’s country.
Q10. What are the common problems in LC transactions? ▶
Common LC challenges include:
- Document discrepancies
- Incorrect LC wording
- Late shipment
- Bank processing delays
- Buyer credit limit issues
Most LC problems arise due to documentation errors, not shipment issues.
Q11. What happens if documents do not comply with LC terms? ▶
If discrepancies are found:
- Bank may refuse payment
- Buyer may accept or reject discrepancies
- Payment may be delayed or renegotiated
Strict compliance with LC terms is critical for successful payment.
Q12. Is a Letter of Credit 100% risk-free? ▶
No. While LCs significantly reduce payment risk, they do not eliminate all risks, such as:
- Fraudulent documents
- Political sanctions
- Force majeure events
- Poorly drafted LC terms
Proper due diligence and professional guidance are essential.
Q13. Under which rules are Letters of Credit governed? ▶
Letters of Credit are governed by UCP 600 (Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits) issued by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC).
Q14. Can exporters get financing against an LC? ▶
Yes. Exporters can obtain:
- Pre-shipment finance
- Post-shipment finance
- Discounting of Usance LC
LCs are widely accepted as bankable trade instruments.
Q15. When should an LC be used instead of advance payment or open account? ▶
An LC is ideal when:
- Trading with new or unknown buyers
- Dealing with high-value shipments
- Operating in high-risk countries
- Buyer requests deferred payment
Forex, Exchange Rates & Hedging
What is Forex & Exchange Rate?
Foreign Exchange (Forex) Market
The Foreign Exchange (Forex) market is the global marketplace where currencies are bought, sold, and exchanged. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, operating 24 hours a day across major financial centers such as London, New York, Tokyo, and Singapore.
In international trade, Forex enables:
- Exporters to convert foreign earnings into domestic currency
- Importers to pay overseas suppliers
- Multinational companies to manage multi-currency cash flows
Exchange Rate
An exchange rate represents the value of one currency relative to another currency (e.g., USD/INR, EUR/USD). Exchange rates may be:
- Fixed (controlled by central banks)
- Floating (market-driven based on demand and supply)
- Managed float (partially regulated by authorities)
Even small exchange rate movements can significantly impact profitability in international trade contracts.
Why Forex & Exchange Rates are Important in International Trade
1. Impact on Export & Import Pricing
- Export competitiveness in global markets
- Import cost fluctuations
A depreciating domestic currency benefits exporters but increases import costs, while an appreciating currency has the opposite effect.
2. Profit Margin Volatility
Unhedged currency exposure can erode profit margins even when sales volumes increase. Exporters often lose profits not due to poor sales, but due to unfavorable exchange rate movements.
3. Financial Planning & Risk Management
- Accurate cost forecasting
- Improved pricing strategy
- Better working capital planning
4. Global Trade Expansion
- Enter new international markets
- Price products competitively
- Offer flexible payment terms to overseas buyers
Where Forex & Exchange Rates are Used
- Export–Import Transactions (invoice settlement in foreign currency)
- Multinational Corporations (MNCs) with overseas operations
- Cross-border investments & joint ventures
- International logistics & freight payments
- Global procurement & sourcing activities
Forex exposure is particularly critical in countries with volatile currencies, emerging markets, or high inflation economies.
Understanding Currency Risk in International Trade
- Transaction Risk – Risk arising from exchange rate movement between contract date and payment date.
- Translation Risk – Risk related to conversion of foreign assets and liabilities into domestic currency for financial reporting.
- Economic Risk – Long-term risk impacting competitiveness and market value due to sustained currency changes.
How to Hedge Currency Risk – Professional Strategies
1. Forward Contracts (Most Common Method)
A forward contract locks in a specific exchange rate for a future date, protecting businesses from adverse currency movements.
Advantages:
- Predictable cash flows
- No upfront cost
- Simple to execute
Limitations:
- No benefit if market moves favorably
Best for: Exporters and importers with fixed payment schedules.
2. Currency Options
Currency options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a predetermined rate.
Advantages:
- Protection against downside risk
- Ability to benefit from favorable movements
Limitations:
- Premium cost involved
Best for: Businesses needing flexibility in uncertain markets.
3. Currency Futures
Standardized contracts traded on exchanges to hedge currency risk.
Advantages:
- Transparent pricing
- Regulated market
Limitations:
- Less customization
- Margin requirements
Best for: Large corporates and financial institutions.
4. Natural Hedging
Natural hedging involves matching foreign currency inflows with outflows, such as:
- Paying overseas suppliers in the same currency as export earnings
- Maintaining foreign currency accounts
Advantages:
- No financial cost
- Reduces dependency on financial instruments
Limitations:
- Limited applicability
Best for: Multinational companies with global operations.
Comparative Overview of Hedging Instruments
| Hedging Tool | Cost | Flexibility | Risk Protection | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward Contract | Low | Low | High | SMEs, Exporters |
| Currency Option | Medium | High | High | Volatile markets |
| Currency Futures | Medium | Medium | High | Corporates |
| Natural Hedging | None | Limited | Medium | MNCs |
Best Practices for Forex & Hedging in Export-Import Business
- Always identify currency exposure at contract stage
- Hedge high-value and long-tenure transactions
- Use professional forex advisory services
- Monitor central bank policies and global economic trends
- Diversify currency exposure across markets
Forex, Exchange Rates & Hedging Process Flowchart

FAQ – Forex, Exchange Rates & Hedging
Q1. What is Forex in international trade? ▶
Definition: Forex (Foreign Exchange) refers to the global market where currencies are exchanged. In international trade, forex enables exporters and importers to receive and make payments in different currencies, making cross-border business possible.
Q2. What is an exchange rate? ▶
Meaning: An exchange rate is the value of one currency in relation to another currency (e.g., USD/INR, EUR/USD). It determines how much domestic currency is required to pay or receive a foreign currency amount.
Q3. Why do exchange rates fluctuate? ▶
- Demand and supply of currencies
- Inflation and interest rates
- Central bank policies
- Political and economic stability
- Global trade and capital flows
These fluctuations directly affect export pricing and import costs.
Q4. What is forex risk in export–import business? ▶
Risk: Forex risk is the possibility of financial loss due to adverse currency movements between the contract date and payment date. Even profitable trade deals can incur losses if currency risk is not managed.
Q5. What are the types of forex risks? ▶
- Transaction Risk: Risk during payment settlement
- Translation Risk: Risk while converting financial statements
- Economic Risk: Long-term impact on competitiveness
Q6. What is currency hedging? ▶
Protection: Currency hedging is a financial strategy used to protect businesses from unfavorable exchange rate movements. It helps stabilize cash flows and profit margins in international trade.
Q7. What is a forward contract in forex hedging? ▶
Hedging Tool: A forward contract allows businesses to lock in an exchange rate for a future date, ensuring certainty in payment or receipt amounts.
Q8. What are currency options and futures? ▶
- Currency Options: Provide the right (not obligation) to buy/sell currency at a fixed rate.
- Currency Futures: Exchange-traded contracts with standardized terms.
Both are used to manage currency volatility.
Q9. What is natural hedging? ▶
Method: Natural hedging involves offsetting foreign currency inflows with outflows, such as paying suppliers in the same currency in which export revenue is received.
Q10. When should exporters hedge their forex exposure? ▶
- Contract value is high
- Payment is deferred
- Currency volatility is high
- Profit margins are thin
Early hedging ensures predictable earnings.
Q11. Is forex hedging mandatory? ▶
Guidance: Forex hedging is not mandatory, but it is highly recommended for businesses engaged in international trade, especially in volatile currency environments.
Q12. What happens if forex risk is not hedged? ▶
- Reduced profit margins
- Unexpected financial losses
- Pricing instability
- Cash flow mismatches
Q13. Who provides forex hedging services? ▶
- Commercial banks
- Authorized dealer banks
- Financial institutions
- Export credit agencies
Q14. How does forex hedging improve business competitiveness? ▶
Advantage: By stabilizing pricing and margins, hedging enables exporters to offer competitive prices, enter long-term contracts, and expand into new markets confidently.
Trade Credit Insurance
What is Trade Credit Insurance?
Trade Credit Insurance (TCI) is a financial risk management solution that protects exporters and businesses against non-payment by buyers. The non-payment may arise due to commercial risks (such as buyer insolvency or prolonged default) or political risks (such as war, currency inconvertibility, import restrictions, or government actions).
Trade Credit Insurance ensures that exporters receive a pre-defined percentage of the invoice value even if the buyer fails to pay, thereby safeguarding cash flow, profitability, and balance sheet stability.
Why Use Trade Credit Insurance?
1. Protection Against Buyer Default
- Buyer bankruptcy
- Prolonged payment delays
- Refusal to pay due to financial distress
2. Expansion into New & Risky Markets
Exporters can safely enter new countries and emerging markets where payment risks are higher, without exposing the business to severe financial losses.
3. Improved Credit Management
Insurers provide credit assessments and buyer risk ratings, helping exporters make informed decisions before extending credit terms.
4. Better Access to Export Financing
- Obtain higher working capital limits
- Access post-shipment finance at better rates
5. Enhanced Competitive Advantage
- Open account terms
- Longer credit periods
- Competitive pricing
Where is Trade Credit Insurance Used?
- Exporters selling on open account or deferred payment terms
- SMEs and large exporters with international receivables
- Emerging markets with weak legal systems
- Countries with political instability or currency controls
- Industries with high-value or recurring export transactions
Understanding Risks Covered Under Trade Credit Insurance
Commercial Risks Covered
- Buyer insolvency or bankruptcy
- Protracted default (non-payment beyond agreed credit period)
- Buyer refusal to accept goods without valid reason
Political Risks Covered
- War, civil unrest, or terrorism
- Import/export bans
- Currency transfer restrictions
- Government intervention or sovereign default
How Does Trade Credit Insurance Work? – Step-by-Step Process
-
Exporter Applies for Insurance Policy
Exporter selects a Trade Credit Insurance provider and applies for coverage based on export volume, buyer profile, and destination countries. -
Buyer Risk Assessment & Credit Limit Approval
Insurer evaluates the financial health of buyers and approves credit limits for each buyer. -
Exporter Ships Goods on Credit
Exporter delivers goods/services under approved credit terms. -
Invoice Monitoring & Payment Collection
Exporter continues normal collection efforts while insurer monitors risk. -
Buyer Defaults on Payment
If payment is not received within the defined waiting period, exporter notifies insurer. -
Claim Submission & Compensation
After verification, insurer compensates up to 80–95% of the insured invoice value.
Types of Trade Credit Insurance Policies
-
Whole Turnover Policy
Covers all buyers and transactions under a single policy.
Best for: Large exporters with diversified buyer base. -
Single Buyer Policy
Covers exports to a specific buyer.
Best for: High-value or strategic buyers. -
Political Risk Insurance
Covers losses due to political events.
Best for: High-risk countries. -
Short-Term Trade Credit Insurance
Covers credit terms up to 180 days.
Best for: Regular trade transactions.
Advantages & Limitations of Trade Credit Insurance
| Aspect | Advantage | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Coverage | Protects against non-payment | Partial coverage only |
| Cash Flow | Improves liquidity | Premium cost |
| Financing | Enhances bankability | Policy compliance required |
| Market Expansion | Supports growth | Credit limits apply |
Best Practices for Using Trade Credit Insurance
- Regularly review buyer credit limits
- Report overdue payments promptly
- Maintain accurate documentation
- Align insurance terms with sales contracts
- Combine insurance with LC or bank guarantees where necessary
Flowchart – Trade Credit Insurance Process
FAQ – Trade Credit Insurance
Q1. What is Trade Credit Insurance? ▶
Trade Credit Insurance protects exporters against non-payment by buyers due to insolvency, prolonged default, or political risks, ensuring financial stability in international trade.
Q2. Who should use Trade Credit Insurance? ▶
Exporters selling on open account or deferred payment terms, especially those operating in new or high-risk markets, should use Trade Credit Insurance.
Q3. What risks are covered under Trade Credit Insurance? ▶
It covers commercial risks (buyer insolvency, payment default) and political risks (war, currency restrictions, government actions).
Q4. How much compensation does the insurer provide? ▶
Typically, insurers compensate 80% to 95% of the insured invoice value, depending on the policy terms.
Q5. Does Trade Credit Insurance help in getting bank finance? ▶
Yes. Insured receivables are considered low-risk assets, helping exporters obtain better working capital and export finance from banks.
Q6. Is Trade Credit Insurance mandatory for exporters? ▶
No, it is not mandatory, but it is highly recommended for exporters dealing with credit sales or international buyers.
Q7. What types of Trade Credit Insurance policies are available? ▶
Common types include Whole Turnover Policy, Single Buyer Policy, Political Risk Insurance, and Short-Term Trade Credit Insurance.
Q8. What happens if a buyer fails to pay? ▶
The exporter files a claim after the waiting period. Once verified, the insurer compensates the exporter as per policy terms.
Q9. What documents are required to file a Trade Credit Insurance claim? ▶
- Commercial invoice
- Shipping documents
- Proof of delivery
- Payment follow-up records
Q10. Can Trade Credit Insurance be used along with LC or forex hedging? ▶
Yes. Trade Credit Insurance works best when combined with Letters of Credit (LC) and forex hedging, creating a strong international risk management framework.
Risks in Advance Payment
What is Advance Payment in International Trade?
Advance Payment refers to a payment method in which the buyer pays the exporter fully or partially before goods or services are delivered. This method transfers most of the financial risk from the seller to the buyer and is commonly requested by exporters when dealing with new buyers, customized products, or high-risk countries.
Advance payment can take multiple forms:
- 100% advance payment
- Partial advance payment with balance on shipment
- Milestone-based advance payment
Why Advance Payment Carries Significant Risks
1. Risk of Non-Delivery of Goods
Once payment is made, the buyer has limited control. The seller may:
- Fail to ship goods
- Delay production
- Deliver goods not matching agreed specifications
2. Supplier Fraud & Bankruptcy Risk
The supplier may:
- Be fraudulent
- Become insolvent after receiving payment
- Disappear or shut operations
3. Quality & Specification Risk
Advance payment does not guarantee:
- Product quality
- Compliance with technical standards
- Timely completion of custom orders
4. International Transfer & Banking Risks
Buyers face risks such as:
- Delays in international wire transfers
- Wrong beneficiary details
- Currency conversion losses
5. Political & Regulatory Risks
Government restrictions, sanctions, or trade bans may prevent delivery even after payment is made.
Where Advance Payment is Commonly Used
- Customized or made-to-order products
- High-value machinery and capital goods
- Digital services and intellectual property
- New supplier or startup exporter relationships
- Countries with limited trade finance access
Advance payments are common where seller bargaining power is strong or financing options are limited.
Risk Comparison: Advance Payment vs Other Payment Methods
| Payment Method | Buyer Risk | Seller Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Advance Payment | Very High | Very Low |
| Letter of Credit | Medium | Medium |
| Documentary Collection | Medium | Medium |
| Open Account | Low | High |
How to Mitigate Risks in Advance Payment
1. Use Escrow Accounts
An escrow service holds funds until:
- Shipment is completed
- Contractual conditions are met
2. Supplier Due Diligence
Before making advance payment:
- Verify company registration and trade license
- Check export history and references
- Conduct factory audits if possible
3. Partial Advance Payment Strategy
Instead of 100% advance:
- Pay 20–40% upfront
- Balance payable after shipment or inspection
4. Combine Advance Payment with LC or Bank Guarantee
- Use Standby LC (SBLC) as payment security
- Request Performance Bank Guarantee
5. Third-Party Inspection & Quality Control
Appoint independent agencies to:
- Inspect goods before shipment
- Verify quantity and quality
Legal & Contractual Safeguards for Advance Payment
- Clearly defined delivery timelines
- Penalty clauses for non-performance
- Refund terms in case of failure
- Jurisdiction and arbitration clauses
Strong contracts provide legal protection in cross-border disputes.
Flowchart – Advance Payment Risk & Mitigation Process
FAQ – Risks in Advance Payment
1. What is advance payment in international trade? ▶
Advance payment is a payment method where the buyer pays fully or partially before goods or services are delivered, transferring most of the risk to the buyer.
2. Why is advance payment considered risky for buyers? ▶
Because the buyer pays before delivery, there is a risk of non-delivery, poor-quality goods, supplier fraud, or supplier insolvency.
3. When is advance payment commonly used? ▶
- Custom-made or high-value goods
- New supplier relationships
- High-risk or restricted countries
4. What are the main risks involved in advance payment? ▶
- Non-shipment of goods
- Supplier bankruptcy
- Quality or specification mismatch
- International transfer delays
5. How can buyers reduce advance payment risks? ▶
- Using escrow accounts
- Conducting supplier due diligence
- Opting for partial advance payment
- Combining with LC or bank guarantee
6. Is 100% advance payment safe for first-time transactions? ▶
No. For first-time transactions, 100% advance payment is highly risky and should be avoided unless supported by strong bank guarantees or escrow mechanisms.
7. Can advance payment be combined with other payment methods? ▶
- Letter of Credit (LC)
- Standby LC (SBLC)
- Performance Bank Guarantee
8. What role do escrow accounts play in advance payment? ▶
Escrow accounts hold funds securely and release payment only after contractual conditions are met, significantly reducing buyer risk.
9. What documents help protect buyers in advance payment? ▶
- Detailed sales contract
- Proforma invoice
- Inspection certificates
- Proof of shipment
10. Is advance payment suitable for all international trades? ▶
No. Advance payment should be used selectively and is best suited for low-volume, custom, or high-risk transactions with proper safeguards in place.
Global Payment Gateways
Secure Cross-Border Payment Solutions for International Trade & E-Commerce
What are Global Payment Gateways?
A Global Payment Gateway is a secure digital platform that enables businesses to accept, process, and settle international payments across borders in multiple currencies using various payment methods such as credit cards, debit cards, bank transfers, and digital wallets.
These gateways act as an intermediary between the buyer, merchant, banks, and card networks, ensuring safe authorization, currency conversion, and settlement of international transactions.
Why Use Global Payment Gateways?
Global Payment Gateways are essential for businesses operating internationally due to the following advantages:
-
Faster International Transactions
- Real-time or near real-time payment processing
- Reduces payment delays compared to traditional banking channels
-
Multi-Currency Acceptance
- Allows buyers to pay in their local currency
- Improves conversion rates and customer confidence
-
Enhanced Payment Security
- Advanced encryption, tokenization, and fraud detection
- Compliance with PCI DSS, SSL, and 3D Secure standards
-
Improved Customer Experience
- Multiple payment options increase checkout success
- Seamless and user-friendly payment interface
-
Global Market Expansion
- Enables businesses to sell in multiple countries without local bank accounts
Where are Global Payment Gateways Used?
Global Payment Gateways are widely used across industries and business models:
- Export–Import Businesses
- Cross-border E-commerce Platforms
- SaaS & Digital Service Providers
- Online Marketplaces
- International Freelancers & Consultants
- Travel, Education, and Subscription-Based Businesses
They are especially critical in high-volume international sales environments and countries with foreign exchange regulations.
How Do Global Payment Gateways Work?
Step-by-Step Payment Process
- Customer Initiates Payment – Buyer selects a product/service and chooses a payment method.
- Payment Data Encryption – Payment information is securely encrypted and transmitted.
- Authorization Request – Gateway sends the transaction request to the issuing bank or card network.
- Currency Conversion (If Required) – Exchange rate applied automatically for cross-border payments.
- Payment Approval or Decline – Issuing bank verifies funds and approves the transaction.
- Settlement to Merchant Account – Funds are settled to the merchant’s bank account after deductions.
Key Features of Global Payment Gateways
- Multi-Currency Pricing & Settlement
- Automatic Forex Conversion
- Multiple Payment Methods
- Fraud Detection & Risk Scoring
- API & Website Integration
- Compliance & Regulatory Controls
- Real-Time Reporting & Reconciliation
Types of Payment Methods Supported
- Credit & Debit Cards (Visa, MasterCard, Amex)
- Bank Transfers (SWIFT, ACH, SEPA)
- Digital Wallets (PayPal, Apple Pay, Google Pay)
- Local Payment Methods (UPI, Alipay, regional wallets)
Regulatory & Compliance Requirements
- KYC (Know Your Customer)
- AML (Anti-Money Laundering)
- PCI DSS Compliance
- Data Protection Laws (GDPR, etc.)
- RBI / Central Bank Regulations (country-specific)
Failure to comply can lead to account suspension, penalties, or fund blockage.
Risks & Challenges in Using Global Payment Gateways
- Foreign exchange volatility
- Chargebacks and disputes
- High transaction and conversion fees
- Regulatory restrictions in certain countries
- Payment failures due to regional banking rules
Best Practices for Using Global Payment Gateways
- Choose gateways with strong global coverage
- Enable local currency pricing
- Monitor transaction analytics regularly
- Maintain clear refund and dispute policies
- Combine with forex hedging strategies for large volumes
Global Payment Gateways vs Traditional Banking
| Aspect | Payment Gateway | Traditional Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Fast | Slow |
| Currency Support | Multi-currency | Limited |
| User Experience | Seamless | Complex |
| Integration | API-based | Manual |
| Cost Transparency | High | Low |
Conclusion
Global Payment Gateways are essential infrastructure for modern international trade, enabling secure, fast, and compliant cross-border transactions. When used strategically, they help businesses expand globally, improve cash flow, and enhance customer trust.
Flowchart – Global Payment Gateway Process
FAQ – Global Payment Gateways
1. What is a global payment gateway? ▶
A global payment gateway is a secure online platform that enables businesses to accept and process cross-border payments in multiple currencies using cards, bank transfers, and digital wallets.
2. Who should use global payment gateways? ▶
Exporters, importers, e-commerce businesses, SaaS providers, freelancers, and global marketplaces that receive international online payments should use global payment gateways.
3. How do global payment gateways handle currency conversion? ▶
The gateway automatically converts the buyer’s currency into the merchant’s settlement currency using real-time exchange rates, including applicable forex margins.
4. Are global payment gateways safe for international transactions? ▶
Yes. Reputed gateways follow PCI DSS standards, use encryption, tokenization, fraud detection, and comply with KYC and AML regulations.
5. What payment methods do global payment gateways support? ▶
They support credit/debit cards, international bank transfers, digital wallets, and region-specific local payment methods.
6. What are the common charges involved in global payment gateways? ▶
Charges may include transaction fees, currency conversion fees, settlement fees, and chargeback fees, varying by country and payment method.
7. What compliance requirements must businesses follow? ▶
Businesses must comply with KYC, AML, PCI DSS, data protection laws (GDPR), and country-specific foreign exchange regulations.
8. Can global payment gateways be used for export-import transactions? ▶
Yes. They are widely used for small to medium export-import payments, especially for digital services, samples, and e-commerce exports.
9. How are disputes and chargebacks handled? ▶
Gateways provide dispute management systems where merchants submit documents to contest chargebacks within defined timelines.
Export Financing Options & Incentives
Empowering Exporters with International Trade Funding & Government Support
What is Export Financing?
Export Financing refers to a range of financial products, credit facilities, and government-backed incentives designed to help exporters fund production, procurement, shipment, and post-shipment operations in international trade. It ensures exporters have sufficient working capital and risk coverage while selling goods and services to overseas buyers.
Export financing is offered by:
- Commercial banks
- Export Credit Agencies (ECAs)
- Government institutions
- Multilateral financial bodies
Why Use Export Financing & Incentives?
Export financing plays a critical role in global trade growth for the following reasons:
-
Improves Cash Flow
- Covers production and procurement costs
- Prevents working capital shortages
-
Enhances Global Competitiveness
- Enables exporters to offer competitive payment terms
- Improves pricing flexibility
-
Reduces Financial & Credit Risk
- Protects against buyer default and delayed payments
-
Enables Access to Government Incentives
- Avail tax benefits, subsidies, and interest concessions
-
Supports SME & New Exporters
- Facilitates entry into new international markets
Where is Export Financing Used?
Export financing is used across:
- Manufacturing exports
- Service exports
- Agri-exports
- Engineering & capital goods
- E-commerce exports
- SMEs and large exporters
It is especially beneficial in:
- Long credit cycles
- High-value export contracts
- New or emerging export markets
Types of Export Financing Options
1. Pre-Shipment Finance (Packing Credit)
Financing provided before shipment to fund:
- Raw materials
- Production
- Packaging & logistics
Available in domestic or foreign currency.
2. Post-Shipment Finance
- Bill discounting
- Invoice financing
- LC negotiation
3. Export Credit
Short-term or medium-term credit extended to overseas buyers, supported by banks or ECAs.
4. Buyer’s Credit
Financing offered to foreign buyers to pay exporters upfront, improving exporter liquidity.
5. Forfaiting & Factoring
- Forfaiting: Non-recourse financing for medium-term exports
- Factoring: Sale of export receivables
Export Incentives & Government Support
Export incentives are designed to promote exports and improve competitiveness.
Common Export Incentives Include:
- Duty drawback schemes
- Export subsidies
- Interest equalization schemes
- Tax exemptions on export income
- Freight & logistics incentives
Benefits of Export Incentives
- Reduces overall export cost
- Improves profit margins
- Encourages market diversification
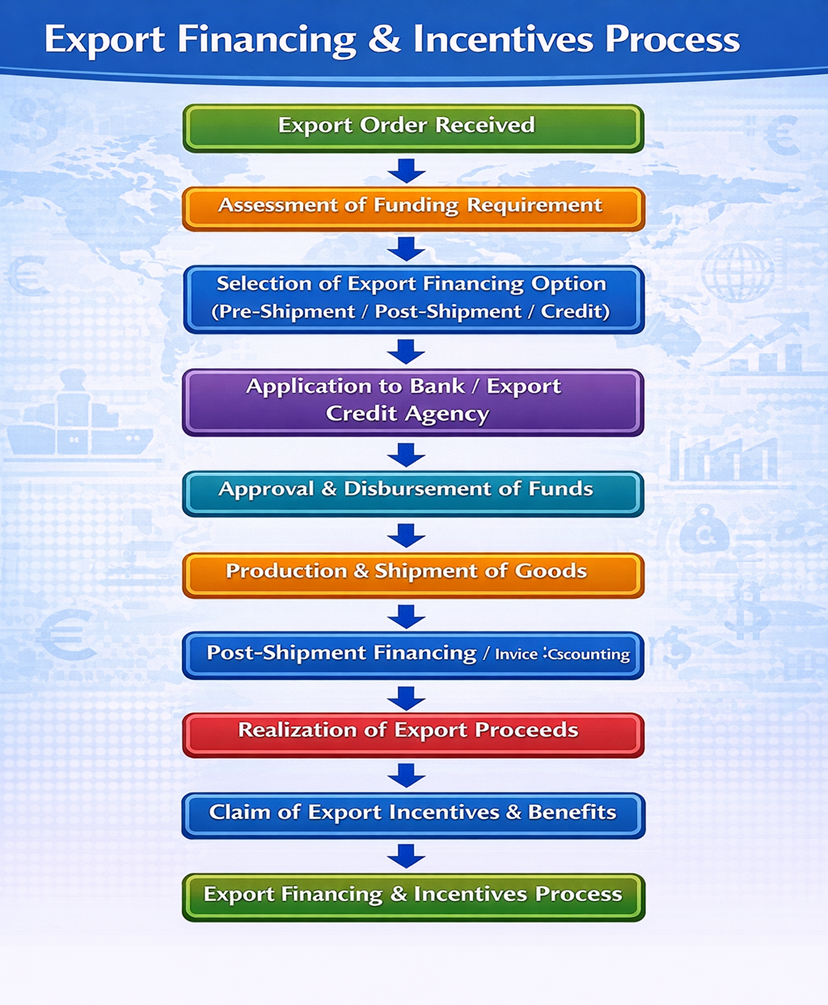
How to Use Export Financing & Incentives Effectively
- Assess export order & funding needs
- Identify suitable financing option
- Approach bank or export credit agency
- Submit export documents & contracts
- Avail finance & incentives
- Execute shipment & realize proceeds
Key Documents Required for Export Financing
- Export contract / purchase order
- Proforma invoice
- Letter of Credit (if applicable)
- Shipping documents
- Exporter KYC documents
Risks & Challenges in Export Financing
- Currency fluctuation risk
- Buyer default risk
- Compliance & documentation errors
- Delays in incentive realization
Mitigation through:
- Hedging
- Trade credit insurance
- Proper compliance management
Flowchart – Export Financing & Incentives Process
Best Practices for Exporters
- Choose financing based on cash flow cycle
- Maintain strong export documentation
- Monitor incentive eligibility regularly
- Combine finance with risk mitigation tools
- Stay updated on government export policies
Conclusion
Export Financing & Incentives are critical enablers of successful international trade, helping exporters manage cash flow, mitigate risk, and expand globally. When used strategically, they significantly improve profitability, sustainability, and competitiveness in global markets.
FAQ – Export Financing Options & Incentives
1. What is export financing? ▶
Export financing refers to financial support and credit facilities that help exporters fund production, shipment, and post-shipment activities in international trade.
2. Who can avail export financing? ▶
Manufacturers, merchant exporters, service exporters, SMEs, startups, and established exporters engaged in international trade can avail export financing.
3. What are the main types of export financing? ▶
The main types include pre-shipment finance, post-shipment finance, export credit, buyer’s credit, factoring, and forfaiting.
4. What is pre-shipment and post-shipment finance? ▶
- Pre-shipment finance funds production and procurement before shipment.
- Post-shipment finance provides liquidity after shipment until payment is received.
5. What are export incentives? ▶
Export incentives are government benefits such as tax exemptions, subsidies, duty drawbacks, and interest support provided to promote exports.
6. How do export incentives benefit exporters? ▶
They reduce export costs, improve profit margins, enhance price competitiveness, and encourage market expansion.
7. What documents are required for export financing? ▶
Common documents include export contracts, invoices, LC (if applicable), shipping documents, and exporter KYC papers.
8. What risks are involved in export financing? ▶
Key risks include buyer default, currency fluctuation, documentation errors, and regulatory delays, which can be managed through insurance and hedging.
9. Is export financing suitable for new exporters? ▶
Yes. Export financing is especially beneficial for new and SME exporters, as it supports working capital needs and reduces financial pressure.