Lean Supply Chain Management
Lean Supply Chain Management is a strategic operational philosophy that focuses on maximizing customer value while systematically eliminating waste across the entire Export–Import (EXIM) ecosystem.
In the context of global trade and international logistics, supply chains are often complex, fragmented, and cost-intensive. Lean principles enable organizations to simplify trade workflows, reduce inefficiencies, strengthen compliance, and improve end-to-end visibility across cross-border operations.
For exporters, importers, and global supply chain operators, lean supply chain management is a critical enabler of competitiveness, profitability, and regulatory resilience.
What is Lean Supply Chain Management?
What is Lean Supply Chain?
Lean Supply Chain Management is a structured, data-driven approach to identifying, analyzing, and eliminating non-value-adding activities (waste) across all supply chain functions, including:
- Procurement & supplier coordination
- Production & order fulfillment
- International logistics & freight movement
- Customs clearance & regulatory compliance
- Warehousing & inventory control
- Distribution & last-mile delivery
In EXIM operations, a lean supply chain ensures that every activity, document, movement, and approval adds measurable value—either to the customer or to regulatory compliance.
Value Creation in Lean EXIM Supply Chains
A lean EXIM supply chain focuses on:
- Speed – reducing lead times and transit delays
- Accuracy – minimizing documentation and compliance errors
- Cost efficiency – lowering logistics, storage, and penalty costs
- Reliability – ensuring predictable and on-time deliveries
Key Outcomes in EXIM Operations
- Faster cargo movement across borders
- Lower logistics, warehousing, and compliance costs
- Reduced customs interventions and penalties
- Higher service reliability and customer trust
- Improved exporter–importer coordination
Why Lean Supply Chain is Important in EXIM?
Complexity of Global Trade
Modern EXIM operations are impacted by:
- Multiple stakeholders (exporters, importers, suppliers, freight forwarders, customs brokers, banks, regulators)
- Complex international trade regulations
- Country-specific compliance requirements
- Volatile freight rates and port congestion
- Extended trade and payment cycles
Without lean practices, these complexities lead to delays, cost overruns, duplication of effort, and compliance risks.
Strategic Importance of Lean in EXIM
Lean supply chain management helps organizations:
- Reduce overall trade cycle time (order to delivery)
- Eliminate duplicate documentation and approvals
- Minimize demurrage, detention, and port storage costs
- Improve working capital through faster cash conversion
- Enhance compliance accuracy and audit readiness
Lean transforms EXIM operations from reactive and fragmented into proactive, predictable, and controlled systems.
Where Lean Principles Apply in EXIM?
Lean principles can be implemented across every stage of the export–import lifecycle, including:
-
Export Operations
- Export order processing
- Shipping instruction preparation
- Documentation verification
- Cargo consolidation and dispatch
-
Import Operations
- Import planning and pre-clearance
- HS code classification
- Customs duty assessment
- Post-clearance compliance
-
Logistics & Transportation
- Freight booking and route optimization
- Carrier and forwarder coordination
- Transit time management
- Exception handling
-
Warehousing & Inventory
- Inventory turnover optimization
- Reduced storage and handling waste
- FIFO/FEFO implementation
- Demand-aligned stocking
-
Compliance & Documentation
- Standardized trade documentation
- Automated data validation
- Regulatory reporting
- Audit preparation
How Lean Supply Chain Works in EXIM?
Lean supply chain management in EXIM follows a continuous improvement cycle focused on visibility, control, and performance.
Step-by-Step Lean Execution Framework
- End-to-End Process Mapping
- Waste Identification
- Root Cause Analysis
- Waste Elimination & Process Optimization
- Standardization of Workflows
- KPI Monitoring & Continuous Improvement
Key Benefits of Lean Supply Chain Management in EXIM
- Reduced logistics and transportation costs
- Shorter order-to-cash cycles
- Lower customs delays and penalties
- Improved shipment predictability
- Enhanced operational transparency
- Stronger compliance governance
- Scalable and resilient global supply chains
Flowchart – Lean Supply Chain Concept
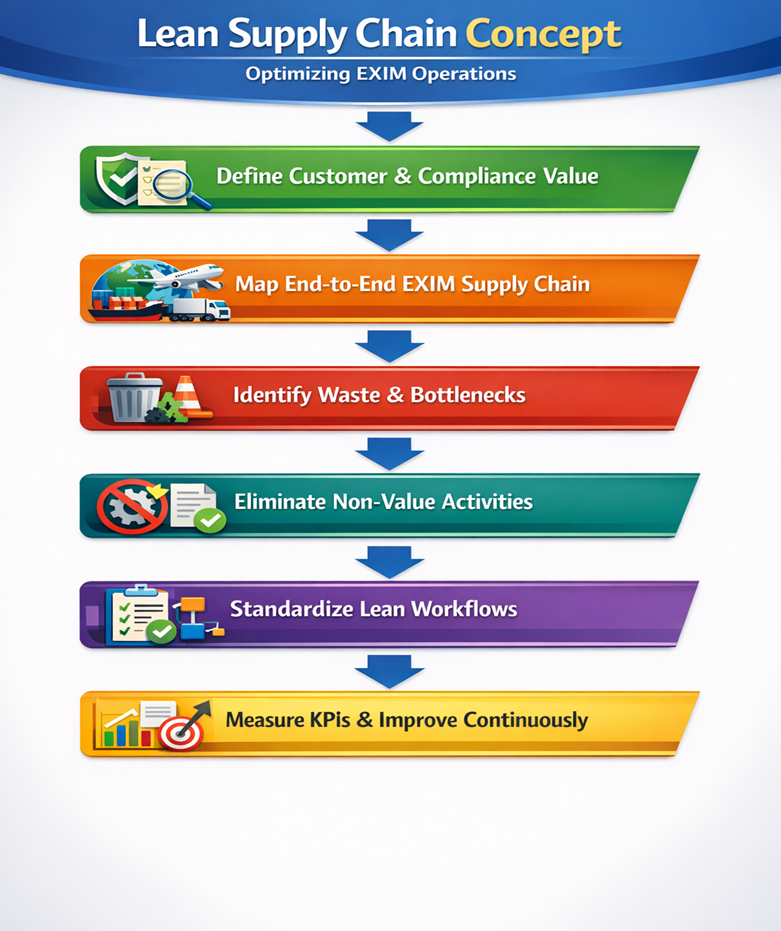
Expert Insight
Lean Supply Chain Management is not a one-time cost-cutting exercise. In EXIM, it is a strategic operating model that aligns speed, compliance, cost efficiency, and customer value into a single integrated system.
Organizations that adopt lean principles gain:
- Faster global market access
- Lower operational risk
- Higher trade profitability
- Long-term competitive advantage
FAQ – Lean Supply Chain Management
1. What is Lean Supply Chain Management? ▶
Lean Supply Chain Management is a strategic approach that focuses on maximizing customer value while eliminating waste across supply chain operations. In EXIM (Export–Import), it improves logistics efficiency, customs compliance, cost control, and delivery speed by removing non-value-adding activities.
2. Why is Lean Supply Chain important in Export-Import (EXIM) operations? ▶
Lean supply chain is critical in EXIM because global trade involves complex documentation, multiple stakeholders, regulatory compliance, and high logistics costs. Lean practices help reduce delays, minimize customs errors, lower costs, and improve trade cycle time, making international operations more competitive.
3. What types of waste are common in EXIM supply chains? ▶
Common EXIM supply chain waste includes:
- Duplicate documentation
- Customs clearance delays
- Excess inventory at ports
- Manual data entry errors
- Unnecessary cargo movement
- Demurrage and detention costs
4. How do Lean tools like 5S, Kaizen, and Kanban help EXIM operations? ▶
Lean tools support structured improvement:
- 5S improves document organization and audit readiness
- Kaizen drives continuous improvement in trade processes
- Kanban provides real-time visibility of shipments and workflows
Together, they enhance accuracy, speed, coordination, and compliance.
5. How does Lean Supply Chain improve customs clearance efficiency? ▶
Lean supply chain improves customs clearance by:
- Standardizing documentation
- Reducing errors in HS codes and declarations
- Enabling pre-clearance planning
- Improving coordination with customs brokers
This results in faster clearance, fewer inspections, and lower penalties.
6. What are the key KPIs used in Lean EXIM Supply Chains? ▶
Key lean supply chain KPIs include:
- Order cycle time
- Customs clearance time
- Logistics cost percentage
- Documentation error rate
- On-time delivery performance
- Inventory turnover
7. How does process standardization support Lean Supply Chain Management? ▶
Process standardization ensures uniform SOPs, templates, and workflows across export-import operations. It reduces errors, improves compliance consistency, speeds up execution, and enables scalability—making lean supply chains predictable and audit-ready.
8. Can small and mid-size exporters implement Lean Supply Chain practices? ▶
Yes. Lean supply chain management is scalable and highly effective for small and mid-size exporters. By focusing on waste reduction, process standardization, and simple KPIs, businesses can achieve cost savings, faster deliveries, and improved compliance without heavy investment.
9. What is the biggest benefit of Lean Supply Chain in global trade? ▶
The biggest benefit of lean supply chain management in global trade is end-to-end visibility combined with cost and risk reduction. It enables organizations to operate faster, smarter, and more compliantly, creating a sustainable competitive advantage in international markets.
Eliminating Waste in EXIM (Lean Waste Framework)
In international trade, waste is one of the biggest hidden cost drivers. Unlike manufacturing, waste in Export–Import (EXIM) operations is often invisible, appearing as delays, rework, compliance errors, excess inventory, and avoidable logistics expenses.
The Lean Waste Framework enables organizations to identify, measure, and systematically eliminate waste across the global trade lifecycle—improving speed, accuracy, compliance, and profitability.
What is Waste in EXIM?
Definition of Waste in Export–Import Operations
In EXIM, waste refers to any activity, process, movement, or delay that consumes time, cost, or resources without adding value to:
- The customer, or
- Regulatory and compliance requirements.
If an activity does not:
- Move cargo closer to delivery, or
- Improve compliance accuracy,
…it is considered non-value-adding waste.
Unique Nature of Waste in EXIM
Unlike manufacturing, EXIM waste is:
- Documentation-heavy
- Regulation-driven
- Multi-stakeholder dependent
- Time-sensitive
This makes waste harder to detect but more expensive to ignore.
Types of Waste in Export–Import Operations (Lean Waste Categories)
Lean supply chain management identifies seven core waste categories, all of which are highly relevant in EXIM.
1. Overprocessing
Definition: Doing more work than required.
EXIM Examples:
- Duplicate documentation across departments
- Manual rechecking of already validated data
- Multiple approvals for routine shipments
Impact:
- Higher administrative costs
- Slower shipment processing
2. Waiting
Definition: Idle time where work or cargo is not moving.
EXIM Examples:
- Cargo waiting for customs examination
- Delay in document approval
- Waiting for freight confirmation
Impact:
- Increased demurrage and detention
- Missed delivery timelines
3. Transportation
Definition: Unnecessary movement of goods.
EXIM Examples:
- Extra port handling
- Re-routing due to poor planning
- Multiple warehouse transfers
Impact:
- Higher freight and handling costs
- Increased risk of damage
4. Inventory
Definition: Excess stock beyond demand.
EXIM Examples:
- Cargo stored at ports due to clearance delays
- Overstocking for uncertain demand
- Slow-moving imported inventory
Impact:
- High storage costs
- Working capital blockage
5. Motion
Definition: Unnecessary movement of people or information.
EXIM Examples:
- Manual data entry across systems
- Physical file movement for approvals
- Searching for documents during audits
Impact:
- Lower productivity
- Higher error probability
6. Defects
Definition: Errors that require correction.
EXIM Examples:
- Incorrect HS code classification
- Wrong country of origin declaration
- Inaccurate invoice values
Impact:
- Customs penalties
- Shipment rejections or holds
7. Overproduction
Definition: Doing work earlier or in larger quantity than required.
EXIM Examples:
- Shipping before confirmed demand
- Preparing export documents without final orders
- Booking cargo prematurely
Impact:
- Excess inventory
- Cash flow inefficiencies
Why Waste Elimination is Critical in EXIM?
Financial Impact
- Reduces logistics, warehousing, and penalty costs
- Improves profit margins on export and import transactions
Compliance Impact
- Enhances accuracy of customs declarations
- Reduces audit observations and penalties
Operational Impact
- Shortens lead times
- Improves shipment predictability
Strategic Impact
- Improves customer satisfaction
- Strengthens competitive advantage in global markets
Flowchart – Waste Elimination in EXIM
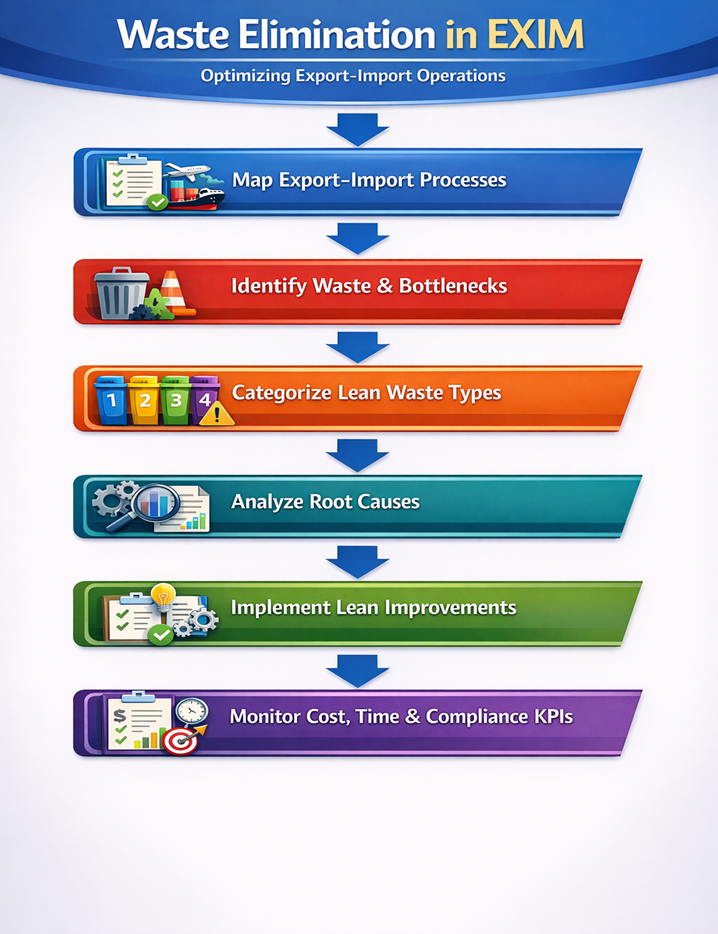
Expert Insight
In EXIM operations, waste is not always visible—but it is always expensive.
Organizations that adopt a lean waste framework gain:
- Faster customs clearance
- Lower logistics costs
- Higher compliance accuracy
- Stronger global competitiveness
Eliminating waste is not about cutting corners—it is about building smarter, faster, and more compliant trade operations.
FAQ – Eliminating Waste in EXIM
1. What does “waste” mean in Export–Import (EXIM) operations? ▶
In EXIM, waste refers to any activity that consumes time, cost, or resources without adding customer or regulatory value. This includes documentation errors, customs delays, excess inventory, manual rework, and unnecessary cargo movement, all of which increase trade costs and risk.
2. Why is eliminating waste critical in international trade? ▶
Eliminating waste is critical because global trade involves tight margins, strict compliance requirements, and time-sensitive logistics. Reducing waste helps organizations lower logistics costs, speed up customs clearance, avoid penalties, and improve overall trade efficiency.
3. What are the most common types of waste in EXIM supply chains? ▶
The most common EXIM waste types include:
- Duplicate documentation (overprocessing)
- Cargo waiting at customs or ports
- Unnecessary cargo transportation
- Excess inventory at ports or warehouses
- Manual data entry and rework
- Incorrect HS codes or declarations
4. How do documentation errors create waste in EXIM? ▶
Documentation errors lead to customs queries, shipment holds, rework, penalties, and delays. Incorrect invoices, packing lists, or HS codes increase clearance time and logistics costs, making documentation accuracy a key focus area for lean EXIM operations.
5. Where does waste occur most frequently in EXIM operations? ▶
Waste most commonly occurs in:
- Export and import documentation preparation
- Customs clearance and compliance checks
- Port and terminal handling
- Warehousing and inventory storage
- Inter-department and partner coordination
6. How can exporters and importers eliminate waste in EXIM? ▶
Organizations can eliminate EXIM waste by:
- Implementing digital documentation and paperless trade
- Automating processes using ERP and trade management systems
- Adopting pre-clearance and advance planning
- Aligning suppliers, freight forwarders, and brokers
- Conducting regular lean audits and reviews
7. How does lean waste elimination improve customs clearance? ▶
Lean waste elimination improves customs clearance by reducing errors, standardizing filings, enabling advance submissions, and improving data accuracy. This results in faster release times, fewer inspections, and lower demurrage and detention costs.
8. Can small and mid-sized exporters apply lean waste reduction in EXIM? ▶
Yes. Lean waste reduction is highly scalable and effective for small and mid-sized exporters. By focusing on process mapping, standard documentation, and simple KPI tracking, businesses can achieve significant cost savings and faster trade cycles without large investments.
9. What is the long-term benefit of eliminating waste in EXIM? ▶
The long-term benefit of eliminating waste in EXIM is the creation of a faster, more compliant, and cost-efficient supply chain. Organizations gain better visibility, stronger risk control, improved customer satisfaction, and sustainable competitive advantage in global markets.
Lean Tools in Supply Chain (5S, Kaizen, Kanban)
Lean tools are structured operational methodologies designed to improve efficiency, accuracy, quality, and workflow continuity across supply chain operations.
In Export–Import (EXIM) environments—where documentation, compliance, coordination, and timing are critical—lean tools help organizations eliminate waste, standardize processes, and maintain operational discipline.
When correctly implemented, lean tools transform EXIM operations from reactive and error-prone into predictable, controlled, and scalable systems.
What are Lean Tools?
Lean tools are practical frameworks and techniques used to:
- Identify inefficiencies
- Eliminate non-value-adding activities
- Improve process flow
- Enhance compliance accuracy
- Enable continuous improvement
In EXIM supply chains, lean tools support faster trade cycles, lower logistics costs, reduced compliance risk, and improved visibility.
Why Lean Tools are Critical in EXIM?
Global trade operations involve:
- High documentation volumes
- Strict regulatory oversight
- Multiple internal and external stakeholders
- Time-sensitive cargo movement
Lean tools provide:
- Process discipline
- Operational transparency
- Error prevention
- Continuous improvement mechanisms
5S in EXIM Operations
What is 5S?
5S is a workplace organization and standardization methodology aimed at creating efficient, clean, and disciplined work environments—both physical and digital.
The five elements of 5S are:
- Sort (Seiri) – Remove what is unnecessary
- Set in Order (Seiton) – Organize what remains
- Shine (Seiso) – Clean and verify
- Standardize (Seiketsu) – Establish consistent procedures
- Sustain (Shitsuke) – Maintain discipline and compliance
In EXIM, 5S applies not only to physical offices and warehouses but also to digital documentation, trade data, and system workflows.
Why 5S Matters in EXIM?
Operational Benefits
5S directly addresses key EXIM challenges by:
- Reducing documentation errors and rework
- Improving file, data, and record accessibility
- Enhancing audit and compliance readiness
- Preventing shipment delays due to missing information
- Improving operational discipline and accountability
Compliance Benefits
- Faster response to customs queries
- Reduced risk of penalties
- Improved traceability of trade records
- Better preparedness for internal and external audits
Where 5S Applies in EXIM Operations?
1. Export Documentation Desks
- Commercial invoices
- Packing lists
- Certificates of origin
- Shipping instructions
2. Customs Compliance Teams
- HS code databases
- Regulatory filings
- License and permit records
3. Warehouse & Logistics Operations
- Inventory labeling
- Storage locations
- Handling equipment organization
4. Shipping & Coordination Offices
- Booking confirmations
- Carrier contracts
- Shipment status tracking
How to Implement 5S in EXIM Operations?
Step-by-Step 5S Implementation Framework
1. Sort (Remove the Unnecessary)
Actions in EXIM:
- Remove outdated document versions
- Archive inactive shipment files
- Eliminate redundant approvals and reports
Outcome:
- Reduced clutter
- Faster access to critical information
2. Set in Order (Organize Systematically)
Actions in EXIM:
- Standard folder structures (by shipment, country, year)
- Clear document naming conventions
- Centralized digital repositories
Outcome:
- Faster document retrieval
- Reduced dependency on individuals
3. Shine (Clean and Validate)
Actions in EXIM:
- Regular data validation
- System cleanup
- Review of master data (HS codes, vendors)
Outcome:
- Fewer errors
- Improved data accuracy
4. Standardize (Define Best Practices)
Actions in EXIM:
- SOPs for export and import documentation
- Standard templates for invoices and packing lists
- Checklist-based compliance reviews
Outcome:
- Consistent execution
- Reduced variability
5. Sustain (Maintain Discipline)
Actions in EXIM:
- Periodic audits
- Compliance reviews
- Performance monitoring
- Training and refreshers
Outcome:
- Long-term operational excellence
- Continuous compliance readiness
Key Benefits of 5S in EXIM
- Faster documentation processing
- Lower error and rework rates
- Reduced shipment delays
- Improved audit outcomes
- Higher team productivity
- Scalable and controlled operations
Flowchart – 5S Implementation in EXIM

Expert Insight
In EXIM operations, disorganization directly translates into delays, penalties, and customer dissatisfaction.
5S is not just a housekeeping tool—it is a foundation for compliance, speed, and reliability in international trade.
Organizations that apply 5S effectively build lean, audit-ready, and high-performing EXIM supply chains.
FAQ: 5S in Lean Supply Chain & EXIM
1. What is 5S in Lean Supply Chain Management? ▶
5S is a lean workplace organization methodology used to improve efficiency, accuracy, and discipline in supply chain and EXIM operations. It stands for Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain, helping organizations eliminate clutter, reduce errors, and improve workflow visibility.
2. Why is 5S important for EXIM operations? ▶
5S is important in EXIM because international trade involves complex documentation, regulatory compliance, and time-critical logistics. Applying 5S helps reduce documentation errors, improve audit readiness, speed up customs clearance, and ensure smooth export-import operations.
3. How does 5S help reduce documentation errors in exports and imports? ▶
5S improves documentation accuracy by sorting unnecessary files, organizing data logically, maintaining clean records, and standardizing formats. This reduces rework, avoids customs queries, and improves compliance accuracy across export and import documentation.
4. Where can 5S be applied in EXIM and logistics operations? ▶
5S can be applied across multiple EXIM touchpoints, including:
- Export and import documentation desks
- Customs compliance teams
- Freight and shipping coordination offices
- Warehouses and inventory control areas
- Trade finance and LC documentation units
5. How is 5S implemented in EXIM organizations? ▶
5S implementation in EXIM involves:
- Sorting and eliminating obsolete physical and digital files
- Creating standard folder structures and naming conventions
- Cleaning and validating trade data regularly
- Documenting SOPs for EXIM workflows
- Conducting periodic audits and reviews
6. What role does 5S play in customs audits and compliance? ▶
5S enhances customs audit readiness by ensuring structured documentation, easy traceability, and standardized records. This reduces compliance risk, supports faster inspections, and helps organizations meet regulatory requirements efficiently.
7. Can 5S be applied to digital systems and ERP in EXIM? ▶
Yes. 5S is highly effective in digital EXIM environments. It helps organize ERP data, standardize document templates, remove redundant entries, and maintain clean master data, improving system efficiency and decision-making.
8. Is 5S suitable for small and medium EXIM businesses? ▶
Absolutely. 5S is cost-effective, scalable, and easy to implement, making it ideal for small and mid-sized exporters and importers. Even basic 5S practices can deliver quick efficiency gains and cost reductions.
9. What are the long-term benefits of 5S in EXIM supply chains? ▶
The long-term benefits of 5S include lower operational costs, faster processing times, improved compliance, higher employee productivity, and better customer satisfaction—all essential for building a lean and resilient global supply chain.
Kaizen (Continuous Improvement) in EXIM & Global Trade
In global trade, change is constant—regulations evolve, logistics conditions fluctuate, and customer expectations rise. Kaizen, meaning continuous incremental improvement, provides a disciplined framework that enables EXIM organizations to adapt continuously, improve performance steadily, and build long-term operational resilience.
Unlike large transformation projects, Kaizen focuses on small, practical improvements implemented consistently by employees at all levels, creating a culture of ongoing excellence in export–import operations.
What is Kaizen?
Definition of Kaizen in Supply Chain & EXIM
Kaizen is a continuous improvement methodology that emphasizes:
- Small, incremental process improvements
- Employee involvement at all levels
- Data-driven decision making
- Standardization of successful practices
In EXIM operations, Kaizen ensures that every shipment, document, and workflow is continuously refined to improve speed, accuracy, cost efficiency, and compliance.
Kaizen Philosophy in Global Trade
Kaizen operates on the principle that: “Many small improvements over time create major competitive advantage.”
In international trade, where margins are tight and risks are high, Kaizen enables organizations to stay compliant, agile, and customer-focused.
Why Kaizen is Essential in Global Trade?
-
Frequent Regulatory Changes
- Customs laws, duties, and trade agreements change regularly
- Non-compliance can lead to penalties and shipment delays
Kaizen ensures continuous adaptation of procedures and controls.
-
Evolving Customer Expectations
- Faster delivery times
- Real-time shipment visibility
- Zero documentation errors
Kaizen supports continuous service improvement without disruption.
-
Volatile Logistics Risks
- Port congestion
- Freight rate fluctuations
- Geopolitical disruptions
Kaizen enables rapid response through incremental process adjustments.
-
Competitive Pressure
- Global markets demand efficiency and reliability
- Lean, agile supply chains outperform rigid systems
Kaizen builds sustainable operational excellence.
Where Kaizen is Applied in EXIM Operations?
Kaizen can be implemented across every EXIM function, including:
-
Export Documentation
- Reducing document preparation time
- Minimizing errors and rework
- Improving data accuracy and consistency
-
Freight Booking & Logistics Planning
- Improving booking lead times
- Optimizing carrier selection
- Reducing transit delays
-
Customs Clearance & Compliance
- Improving HS code accuracy
- Reducing customs queries
- Faster clearance cycles
-
Vendor & Partner Coordination
- Better communication with forwarders and brokers
- Standardized data exchange
- Improved SLA performance
-
Internal Coordination
- Faster approvals
- Reduced handover delays
- Clear accountability
How Kaizen Works in EXIM?
Kaizen follows a structured improvement cycle focused on learning, execution, and standardization.
-
Step 1: Identify Improvement Opportunities
Sources in EXIM:
- Shipment delays
- Customs rejections
- Customer complaints
- Audit observations
- KPI underperformance
-
Step 2: Analyze Root Causes
Common EXIM root causes:
- Manual data handling
- Unclear SOPs
- Poor system integration
- Lack of training
-
Step 3: Implement Small, Practical Changes
Examples:
- Updating a document checklist
- Automating a data validation step
- Redefining approval timelines
-
Step 4: Measure Impact
Key metrics:
- Cycle time reduction
- Error rate improvement
- Cost savings
- Compliance accuracy
-
Step 5: Standardize Successful Improvements
- Update SOPs
- Train teams
- Embed changes into systems
-
Step 6: Repeat Continuously
Kaizen is ongoing—not a one-time initiative.
Kaizen vs Traditional Improvement in EXIM
| Traditional Approach | Kaizen Approach |
|---|---|
| Large, infrequent changes | Small, continuous improvements |
| Top-down execution | Employee-driven participation |
| High disruption | Low disruption |
| Slow adaptation | Fast adaptability |
Key Benefits of Kaizen in EXIM
- Shorter export-import cycle times
- Lower logistics and compliance costs
- Improved customs clearance efficiency
- Higher customer satisfaction
- Stronger compliance culture
- Continuous operational excellence
Flowchart – Kaizen Cycle in EXIM
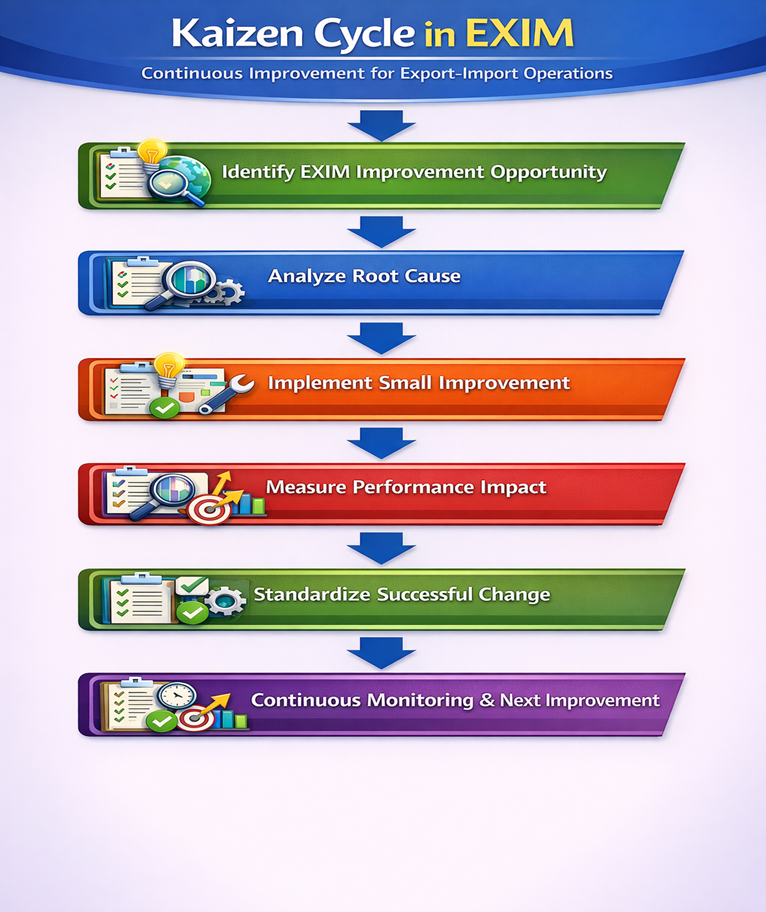
Expert Insight
In global trade, standing still is the fastest way to fall behind. Kaizen empowers EXIM organizations to improve every shipment, every document, and every process—every day. By embedding Kaizen into EXIM operations, organizations achieve:
- Long-term compliance stability
- Cost-efficient trade execution
- Agile response to market and regulatory changes
FAQ – Kaizen in Lean Supply Chain & EXIM
1. What is Kaizen in Lean Supply Chain Management? ▶
Kaizen is a continuous improvement methodology that focuses on making small, incremental changes to improve efficiency, quality, and consistency in supply chain and EXIM operations. In international trade, Kaizen helps optimize workflows across documentation, logistics, customs clearance, and vendor coordination.
2. Why is Kaizen important for export–import operations? ▶
Kaizen is critical in EXIM because trade regulations, logistics risks, and customer expectations change frequently. Continuous improvement enables organizations to adapt quickly, reduce errors, control costs, and maintain compliance in dynamic global trade environments.
3. How does Kaizen help improve customs clearance and compliance? ▶
Kaizen improves customs clearance by identifying recurring errors, reducing rework, standardizing documentation, and improving coordination with customs brokers. This leads to faster clearance times, fewer inspections, and lower compliance risk.
4. Where can Kaizen be applied in EXIM supply chains? ▶
Kaizen can be applied across all EXIM functions, including:
- Export and import documentation processes
- Freight booking and shipment planning
- Customs clearance and regulatory compliance
- Vendor, forwarder, and carrier coordination
- Trade finance and LC processing
5. How does the Kaizen process work in EXIM operations? ▶
The Kaizen cycle in EXIM typically follows four steps:
- Identify improvement opportunities
- Implement small, low-risk changes
- Measure performance impact using KPIs
- Standardize successful improvements
This ensures continuous, sustainable optimization.
6. How is Kaizen different from major process reengineering in EXIM? ▶
Unlike large-scale transformations, Kaizen focuses on incremental, employee-driven improvements. It minimizes disruption while delivering consistent performance gains in cost, speed, and quality across export-import operations.
7. Can Kaizen be implemented by small and mid-sized EXIM companies? ▶
Yes. Kaizen is highly scalable and cost-effective, making it ideal for SMEs. Small exporters and importers can start with simple improvements in documentation accuracy, workflow coordination, and shipment tracking to achieve measurable benefits.
8. What role do employees play in Kaizen-based EXIM improvement? ▶
Employees are central to Kaizen. Since they work closest to EXIM processes, their insights help identify inefficiencies, suggest improvements, and sustain operational discipline—creating a culture of continuous improvement.
9. What are the long-term benefits of Kaizen in EXIM supply chains? ▶
Long-term Kaizen benefits include lower trade costs, faster cycle times, improved compliance accuracy, higher customer satisfaction, and stronger operational resilience—all critical for sustainable success in global trade.
Kanban in Supply Chain & Logistics (EXIM Focus)
In global trade, lack of visibility and poor coordination are among the biggest causes of shipment delays, documentation errors, and compliance failures. Kanban, a visual workflow management system, enables EXIM organizations to control work-in-progress (WIP), optimize process flow, and enhance real-time visibility across export–import operations. When applied to supply chain and logistics, Kanban transforms complex EXIM workflows into transparent, predictable, and manageable processes.
What is Kanban?
Definition of Kanban in Supply Chain
Kanban is a visual process control methodology that manages work by:
- Visualizing tasks and workflows
- Limiting work-in-progress
- Ensuring continuous and balanced flow
- Identifying bottlenecks early
In EXIM supply chains, Kanban helps track shipments, documents, customs stages, and logistics activities in real time.
Kanban Philosophy in Global Trade
Kanban operates on the principle:
“Start work only when capacity is available.”
This is critical in EXIM operations, where overloading teams or systems directly leads to errors, delays, and compliance risks.
Why Use Kanban in EXIM?
-
Improved Shipment Visibility
- Real-time view of shipment status
- Clear understanding of pending and completed tasks
- Reduced dependency on follow-ups and emails
-
Control of Task Overload
- Limits work-in-progress
- Prevents teams from handling too many shipments at once
- Improves accuracy and focus
-
Bottleneck Identification & Prevention
- Highlights delays in customs clearance
- Identifies documentation backlogs
- Enables faster corrective actions
-
Enhanced Cross-Functional Coordination
- Aligns exporters, logistics teams, customs brokers, and warehouses
- Improves accountability and ownership
- Strengthens collaboration across EXIM stakeholders
Where Kanban is Used in EXIM Operations?
-
Shipment Tracking & Control
- Export shipment status monitoring
- Import arrival and clearance tracking
- Exception management
-
Documentation Workflow Management
- Invoice and packing list preparation
- Certificate and license approvals
- Compliance checks
-
Customs Clearance Stages
- Pre-clearance
- Filing
- Examination
- Duty payment
- Release
-
Warehouse & Dispatch Planning
- Cargo receipt
- Picking and packing
- Dispatch scheduling
- Inventory movement
How Kanban Works in EXIM?
Kanban uses visual boards and cards to represent work items and workflow stages.
Core Components of Kanban
-
Visual Boards
- Physical or digital dashboards
- Represent end-to-end EXIM workflows
-
Kanban Cards
- Each card represents a shipment, document, or task
- Contains key trade information (shipment ID, customer, due date)
-
Workflow Columns
- Clearly defined process stages
- Example: “Pending → In Progress → Under Customs → Released”
-
Work-In-Progress (WIP) Limits
- Maximum number of tasks allowed per stage
- Prevents congestion and overload
-
Real-Time Updates
- Status updates as tasks progress
- Immediate visibility of issues
Typical EXIM Kanban Columns
- Shipment Requested
- Documentation in Progress
- Ready for Customs
- Customs Clearance
- Cleared / Released
- Dispatched / Delivered
Key Benefits of Kanban in EXIM Supply Chains
- Faster export-import cycle times
- Reduced documentation and compliance errors
- Improved on-time delivery performance
- Higher team productivity
- Stronger operational transparency
- Better customer communication
Best Practices for Implementing Kanban in EXIM
- Start with one EXIM process (e.g., export documentation)
- Define clear workflow stages
- Set realistic WIP limits
- Use digital Kanban tools integrated with ERP
- Review boards daily
- Continuously refine workflows
Flowchart – Kanban Workflow in EXIM
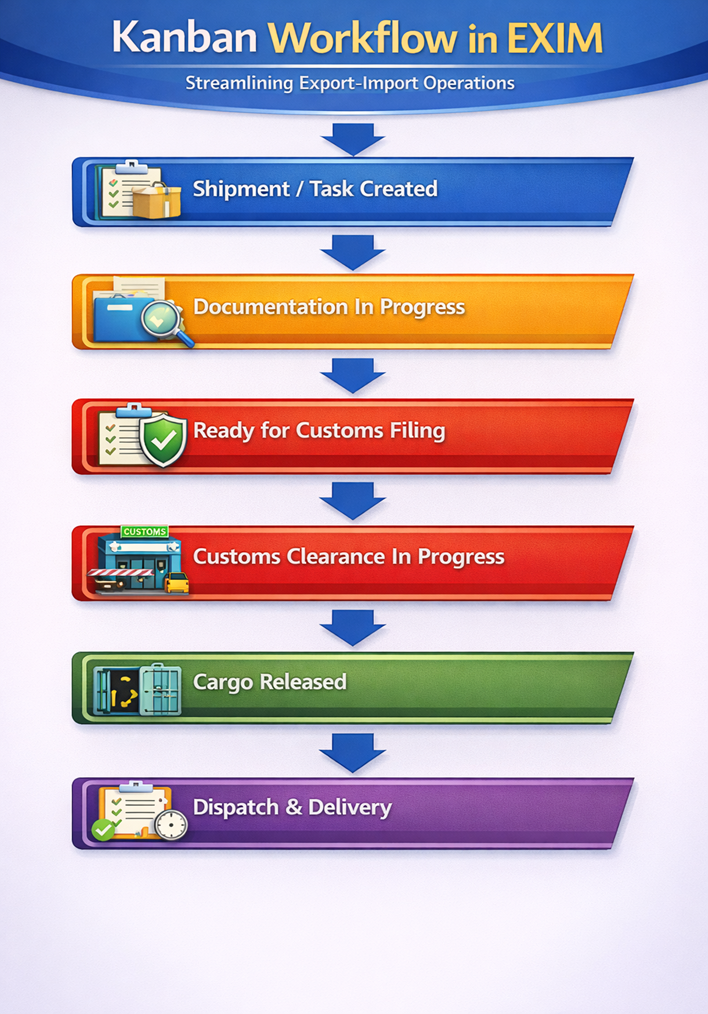
Expert Insight
In EXIM operations, what is not visible cannot be controlled. Kanban provides the real-time visibility and flow control required to manage complex global trade operations efficiently. When combined with 5S and Kaizen, Kanban becomes a powerful enabler of lean, agile, and compliant EXIM supply chains.
FAQ - Kanban in Lean Supply Chain & EXIM
1. What is Kanban in Lean Supply Chain Management? ▶
Kanban is a visual workflow management system used to control work-in-progress (WIP) and improve process flow across supply chain and EXIM operations. In international trade, Kanban helps teams track shipments, documents, and clearance stages in real time.
2. Why is Kanban important for EXIM and logistics operations? ▶
Kanban is important in EXIM because export-import processes involve multiple handoffs, dependencies, and timelines. Kanban improves visibility, prevents task overload, reduces bottlenecks, and enhances coordination between documentation, logistics, and customs teams.
3. How does Kanban improve shipment visibility in international trade? ▶
Kanban improves shipment visibility by providing real-time status tracking of tasks such as document preparation, cargo booking, customs clearance, and delivery. This allows stakeholders to identify delays early and take corrective action.
4. Where can Kanban be applied in EXIM supply chains? ▶
- Export and import documentation workflows
- Shipment and freight booking stages
- Customs clearance processes
- Warehouse dispatch and delivery planning
- Vendor and carrier coordination
5. How does Kanban help reduce delays and bottlenecks in EXIM? ▶
Kanban reduces delays by limiting work-in-progress, highlighting blocked tasks, and balancing workload across teams. Bottlenecks become visible instantly, enabling faster resolution and smoother trade flow.
6. How does a Kanban workflow work in EXIM operations? ▶
- Visual boards (physical or digital)
- Status columns such as “Pending,” “In Progress,” “Under Customs,” and “Completed”
- Task cards representing shipments or documents
- Continuous updates to maintain flow
7. Can Kanban be integrated with ERP and digital trade systems? ▶
Yes. Kanban works effectively with ERP, TMS, and logistics management systems. Digital Kanban boards improve data accuracy, enhance collaboration, and support real-time decision-making in export-import operations.
8. Is Kanban suitable for small and mid-sized EXIM companies? ▶
Absolutely. Kanban is simple, scalable, and cost-effective, making it ideal for SMEs. Even basic Kanban boards can significantly improve task visibility, reduce errors, and enhance delivery reliability.
9. What are the long-term benefits of using Kanban in EXIM supply chains? ▶
Long-term benefits include improved delivery reliability, lower operational costs, faster trade cycles, better team coordination, and higher customer satisfaction, creating a resilient and lean global supply chain.
Standardizing & Streamlining EXIM Processes
In Export–Import (EXIM) operations, process inconsistency is one of the biggest causes of errors, delays, and compliance risks.
Standardizing and streamlining EXIM processes means designing uniform, repeatable, and controlled workflows that ensure speed, accuracy, and regulatory compliance across global trade transactions.
A standardized EXIM operating model transforms trade operations from person-dependent and reactive into system-driven, scalable, and audit-ready processes.
What is Process Standardization in EXIM?
Definition
Process standardization in EXIM refers to the creation and enforcement of uniform procedures, templates, formats, and workflows for all export and import activities, regardless of:
- Product category
- Destination or origin country
- Business unit
- Shipment volume
It ensures that every trade transaction follows the same approved method, minimizing variability and risk.
Standardization vs Streamlining
- Standardization focuses on consistency
- Streamlining focuses on efficiency
Together, they create lean, fast, and compliant EXIM operations.
Why Standardization is Critical in EXIM?
-
Error Reduction & Accuracy Improvement
- Eliminates manual interpretation
- Reduces documentation mismatches
- Minimizes rework and corrections
-
Regulatory & Customs Compliance
- Ensures consistent HS code usage
- Supports accurate customs declarations
- Improves audit and inspection outcomes
-
Faster Trade Execution
- Reduces processing time per shipment
- Enables parallel task execution
- Improves shipment turnaround time
-
Scalability & Business Growth
- Supports higher shipment volumes
- Enables onboarding of new team members quickly
- Facilitates expansion into new markets
-
Risk Mitigation
- Reduces dependency on individuals
- Improves continuity during staff changes
- Strengthens governance and control
Where Standardization Applies in EXIM Operations?
Standardization must be applied across all core EXIM touchpoints, including:
-
Commercial Invoices
- Standard invoice formats
- Consistent value declarations
- Unified product descriptions
- Currency and Incoterms alignment
-
Packing Lists
- Standard quantity and weight formats
- Uniform packaging descriptions
- Alignment with invoice and BL
-
Shipping Instructions
- Standard data fields
- Consistent carrier instructions
- Automated data sharing with forwarders
-
Customs Declarations
- Standard HS code libraries
- Duty calculation logic
- Country-specific compliance rules
-
Trade Finance Documentation
- Letters of Credit (LC)
- Bank negotiation documents
- Insurance certificates
- Payment and settlement records
How to Standardize EXIM Processes?
Step-by-Step Standardization Framework
Step 1: Define EXIM SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures)
Actions:
- Document export and import workflows
- Define roles and responsibilities
- Establish approval hierarchies
Outcome:
- Clear, repeatable processes
- Reduced ambiguity
Step 2: Develop Standardized Templates
Key Templates:
- Commercial invoices
- Packing lists
- Shipping instructions
- Compliance checklists
Outcome:
- Consistency across shipments
- Reduced documentation errors
Step 3: Implement ERP & Trade Management Systems
Capabilities:
- Centralized data management
- Automated validations
- Real-time process visibility
Outcome:
- Reduced manual work
- Integrated workflows
Step 4: Train Teams & External Partners
Focus Areas:
- SOP adherence
- System usage
- Compliance awareness
Outcome:
- Uniform execution
- Improved coordination
Step 5: Conduct Audits & Continuous Improvements
Activities:
- Internal audits
- Compliance reviews
- Process refinement
Outcome:
- Sustained standardization
- Continuous optimization
Key Benefits of Standardized & Streamlined EXIM Processes
- Faster export-import cycle times
- Lower documentation and compliance errors
- Reduced customs delays and penalties
- Improved audit readiness
- Enhanced operational control
- Scalable global trade operations
Flowchart – Standardized EXIM Process

Expert Insight
In global trade, speed without standardization creates risk, and standardization without streamlining creates rigidity.
Successful EXIM organizations balance both—building efficient, compliant, and scalable trade processes.
Standardizing EXIM operations is not just an operational improvement; it is a strategic foundation for sustainable international growth.
FAQ – Standardizing & Streamlining EXIM Processes
1. What does standardizing EXIM processes mean? ▶
Standardizing EXIM processes means creating uniform procedures, templates, and workflows for all export-import activities such as documentation, customs filing, logistics coordination, and trade finance. It ensures consistency, accuracy, and compliance across global trade operations.
2. Why is process standardization critical in export–import operations? ▶
Process standardization is critical because EXIM involves complex regulations, multiple stakeholders, and high compliance risk. Standardized workflows reduce errors, speed up operations, improve audit readiness, and ensure regulatory compliance across markets.
3. How does streamlining EXIM processes improve operational efficiency? ▶
Streamlining removes unnecessary steps, duplication, and manual effort from EXIM workflows. This leads to faster documentation, quicker customs clearance, lower logistics costs, and improved supply chain responsiveness.
4. Which EXIM documents benefit most from standardization? ▶
The documents that benefit most include:
- Commercial invoices
- Packing lists
- Shipping instructions
- Bills of lading / airway bills
- Customs declarations
- Letters of Credit and trade finance documents
Standard formats reduce discrepancies and clearance delays.
5. Where should organizations apply standardized EXIM workflows? ▶
Standardized workflows should be applied across:
- Export order processing
- Import customs clearance
- Logistics and freight booking
- Vendor and carrier coordination
- Compliance and audit management
This ensures end-to-end trade consistency.
6. How can companies standardize and streamline EXIM processes? ▶
Companies can standardize EXIM processes by:
- Defining detailed SOPs for each trade activity
- Using standardized document templates
- Implementing ERP and trade management systems
- Training teams regularly
- Conducting internal audits and reviews
7. How does standardization help with customs compliance and audits? ▶
Standardization ensures accurate, complete, and traceable documentation, making customs audits smoother and reducing the risk of penalties. It also supports faster inspections and regulatory approvals.
8. Can small and mid-sized EXIM businesses benefit from process standardization? ▶
Yes. Standardization is highly beneficial for SMEs, as it improves efficiency without heavy investment. Simple SOPs and templates help small exporters and importers scale operations while maintaining compliance.
9. What are the long-term benefits of standardizing EXIM processes? ▶
Long-term benefits include reduced errors, faster trade cycles, lower operating costs, improved compliance, enhanced visibility, and better customer satisfaction, enabling sustainable growth in global markets.
Visibility KPIs & Performance Dashboards
In modern Export–Import (EXIM) operations, visibility is the foundation of control. Without accurate, real-time performance data, organizations cannot identify risks, control costs, or improve efficiency.
Visibility KPIs and Performance Dashboards provide a data-driven framework to measure, monitor, and continuously improve speed, cost, quality, and compliance across global supply chains.
In a lean supply chain, KPIs convert operational data into actionable insights, enabling proactive decision-making rather than reactive firefighting.
What are Supply Chain KPIs?
Definition
Supply Chain Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are quantifiable metrics used to evaluate how effectively an organization manages its supply chain activities across:
- Export and import operations
- Logistics and transportation
- Customs clearance and compliance
- Inventory and warehousing
- Vendor and partner performance
In EXIM, KPIs act as early-warning signals, highlighting delays, inefficiencies, cost overruns, and compliance risks before they escalate.
Role of KPIs in Lean EXIM Operations
Lean supply chains rely on:
- Measurement
- Transparency
- Continuous improvement
KPIs ensure that:
- Only value-adding activities are optimized
- Waste and bottlenecks are identified quickly
- Performance improvements are measurable and sustainable
Why KPIs are Critical in Lean Supply Chain Management?
-
Data-Driven Decision Making
- Eliminates guesswork
- Supports fact-based operational and strategic decisions
- Improves forecasting and planning accuracy
-
Early Risk Detection
- Identifies customs delays and compliance deviations
- Flags cost overruns and service failures
- Enables proactive corrective actions
-
Performance Benchmarking
- Compares performance across:
- Countries
- Carriers
- Freight forwarders
- Vendors
- Supports continuous improvement initiatives
-
Continuous Improvement & Lean Governance
- Measures impact of lean initiatives
- Supports Kaizen and waste-reduction programs
- Reinforces accountability and ownership
Key EXIM Lean KPIs (Detailed Framework)
| KPI | Description | Lean Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Order Cycle Time | Time from order confirmation to delivery | Speed |
| Customs Clearance Time | Time taken for customs release | Efficiency |
| Logistics Cost (%) | Logistics cost as % of order value | Cost control |
| Documentation Error Rate | Errors per shipment | Quality |
| On-Time Delivery (OTD) | Shipments delivered on schedule | Reliability |
| Inventory Turnover | Inventory movement frequency | Optimization |
Additional Advanced EXIM KPIs
- Demurrage & Detention Cost
- Customs Query Rate
- Compliance Deviation Rate
- Freight Rate Variance
- Vendor SLA Adherence
- Order-to-Cash Cycle Time
Where Performance Dashboards are Used in EXIM?
-
Management Review & Strategic Planning
- Executive dashboards
- Monthly and quarterly performance reviews
- Cost and profitability analysis
-
Compliance Monitoring
- Customs and regulatory KPIs
- Audit readiness tracking
- Risk exposure analysis
-
Logistics & Operations Planning
- Shipment status visibility
- Bottleneck identification
- Resource and capacity planning
-
Vendor & Partner Performance Evaluation
- Freight forwarder performance
- Carrier reliability
- Broker and warehouse SLA compliance
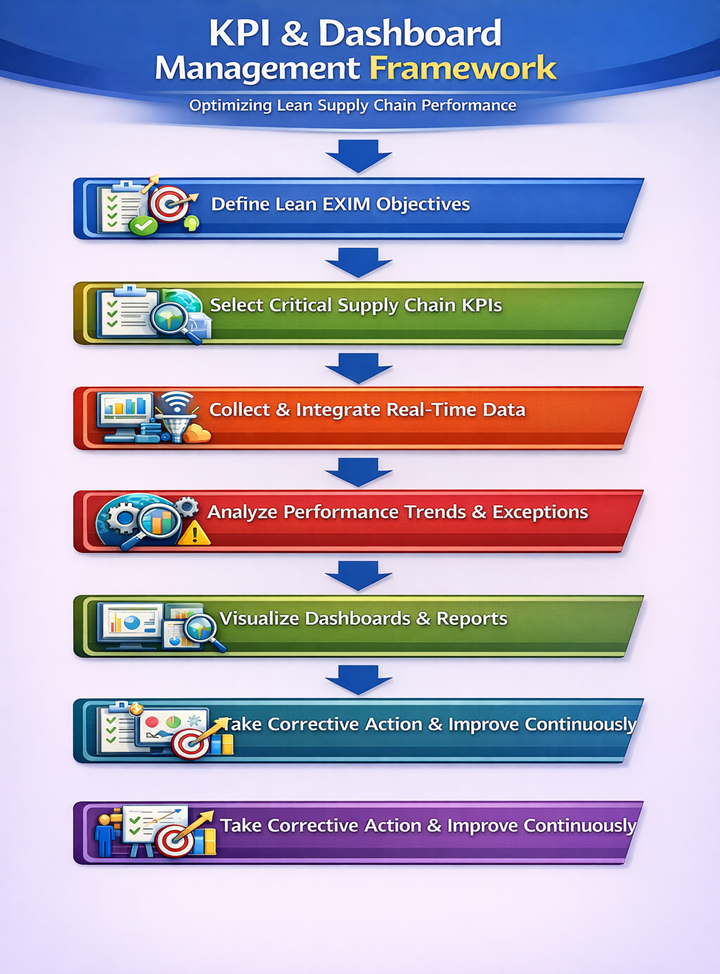
How to Build Effective EXIM Performance Dashboards?
Step-by-Step Dashboard Development Framework
-
Step 1: Identify Critical EXIM KPIs
Focus on KPIs that directly impact:
- Cost
- Speed
- Compliance
- Customer satisfaction
Avoid KPI overload—clarity over quantity.
-
Step 2: Integrate ERP & Logistics Data
Key data sources include:
- ERP systems
- Trade management software
- Logistics and freight platforms
- Customs clearance systems
-
Step 3: Enable Real-Time Visualization
Use:
- Interactive dashboards
- Trend analysis
- Exception alerts
Ensure dashboards are role-based (management, operations, compliance).
-
Step 4: Define Ownership & Review Frequency
- Assign KPI ownership
- Conduct weekly/monthly reviews
- Track corrective actions
-
Step 5: Link KPIs to Continuous Improvement
- Feed KPI insights into Kaizen initiatives
- Update SOPs and workflows
- Measure improvement impact
Best Practices for KPI & Dashboard Management in EXIM
- Align KPIs with business and compliance goals
- Use standardized definitions across teams
- Automate data capture wherever possible
- Focus on actionable insights, not just reporting
- Continuously refine KPIs as trade conditions change
Flowchart – KPI & Dashboard Management Framework
Expert Insight
In EXIM operations, what gets measured gets improved—and what is not visible becomes a risk. Visibility KPIs and performance dashboards transform supply chains from reactive cost centers into strategic, data-driven value creators.
Organizations that master EXIM analytics achieve:
- Faster trade cycles
- Lower logistics and compliance costs
- Stronger risk management
- Sustainable competitive advantage
FAQ – Visibility KPIs & Performance Dashboards in EXIM
1. What are visibility KPIs in EXIM supply chain management? ▶
Visibility KPIs in EXIM are measurable performance indicators that track the speed, cost, accuracy, and compliance of export-import operations. They provide real-time insight into shipments, documentation, customs clearance, and logistics performance.
2. Why are KPIs critical in a lean EXIM supply chain? ▶
KPIs are critical because lean EXIM supply chains rely on data-driven decision-making. Visibility KPIs help identify delays, detect risks early, control costs, benchmark performance, and support continuous improvement across global trade operations.
3. What are the most important KPIs for export-import operations? ▶
Key EXIM KPIs include:
- Order cycle time
- Customs clearance time
- Logistics cost percentage
- Documentation error rate
- On-time delivery performance
- Inventory turnover
These KPIs measure speed, efficiency, quality, and reliability.
4. How do performance dashboards improve supply chain visibility? ▶
Performance dashboards centralize KPI data into real-time visual reports, enabling faster decision-making. They help stakeholders monitor shipments, track exceptions, and respond quickly to delays or compliance issues.
5. Where are EXIM performance dashboards commonly used? ▶
EXIM dashboards are commonly used in:
- Management and leadership reviews
- Logistics and shipment planning teams
- Customs compliance monitoring
- Vendor and carrier performance evaluation
They ensure end-to-end trade transparency.
6. How do KPIs support customs compliance and risk management? ▶
KPIs such as clearance time, error rate, and inspection frequency help identify compliance risks early. Monitoring these metrics improves audit readiness, reduces penalties, and ensures regulatory adherence.
7. How can organizations build effective EXIM performance dashboards? ▶
To build effective dashboards, organizations should:
- Identify critical EXIM KPIs
- Integrate ERP, TMS, and customs data
- Use real-time visualization tools
- Review dashboards regularly for improvement
8. Can small and mid-sized EXIM businesses use KPI dashboards? ▶
Yes. KPI dashboards are scalable and cost-effective, making them suitable for SMEs. Even basic dashboards provide valuable insights into shipment performance, costs, and compliance.
9. What are the long-term benefits of visibility KPIs in EXIM? ▶
Long-term benefits include improved operational control, faster trade cycles, reduced costs, better compliance, higher customer satisfaction, and continuous performance improvement in global supply chains.